In the simplest terms, a stockbroker (share broker) is an individual or a firm that helps investors buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other securities. Whether you’re a seasoned investor seeking sophisticated strategies or a newcomer aiming to grow your savings, a stockbroker can act as your gateway to the financial markets.
Stockbrokers are regulated professionals who execute trades on behalf of clients. They offer a variety of services, ranging from research and financial advice to portfolio management and trade execution. As the financial world grows more complex, stockbrokers provide essential expertise that can help you navigate ever-changing market conditions.
Importance of Stockbrokers
- Smooth Trading Process: By charging fees or commissions on executed trades, stockbrokers ensure that transactions are carried out efficiently.
- Market Liquidity: They bridge the gap between buyers and sellers, which helps maintain liquidity and transparency.
- Investor Confidence: Reputable stockbrokers follow strict regulatory guidelines, boosting trust in the market.
Choosing the Right Stockbroke
- Service Offerings: Determine whether you need research, advisory services, or basic trade execution.
- Fee Structure: Understand the commissions and fees they charge for their services.
- Regulatory Compliance: Make sure they adhere to guidelines and have a strong reputation.
- Investment Approach: Consider whether you’re pursuing short-term trading strategies or long-term investments.
Before opening an account, it’s essential to compare fees, trading platforms, and available markets. Get an overview of the best trading platforms in our broker review to find the one that suits your needs.
Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
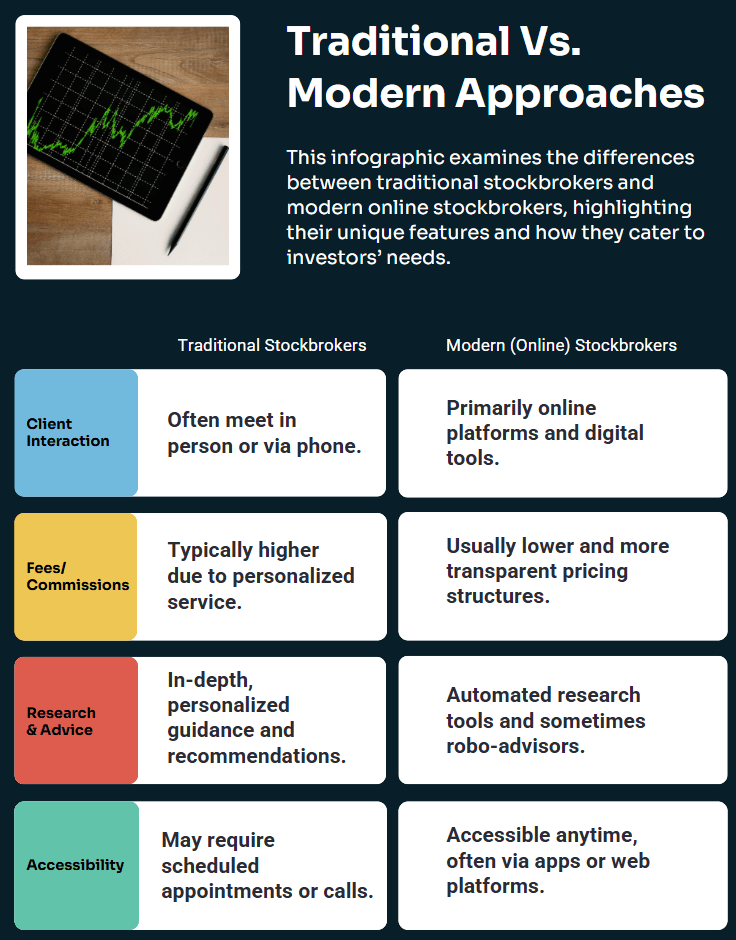
This article delves deeper into the various responsibilities of stockbrokers, their types, and how to choose the right one. We will explore both traditional and modern approaches, highlight the essential compliance measures they follow, and offer insights into the future of stockbroking.
By the end, you’ll grasp why stockbrokers remain such an integral part of financial markets worldwide. Whether you’re focusing on a short-term trading strategy or a long-term investment approach, understanding the function of a stockbroker can be your first step toward confident market participation.
Understanding the Basics of a Stockbroker (share broker)
Before diving into the finer details of the profession, it’s crucial to understand the basics of a stockbroker (share broker) and how their role fits into the broader financial system. A stockbroker primarily acts as a middleman between you—the investor—and the stock exchange. Different jurisdictions have varying rules that require trades to be conducted through registered brokers. This makes stockbrokers indispensable when it comes to buying or selling shares.
These professionals undergo rigorous examinations and licensing procedures, such as the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) exams in the United States, to demonstrate their competence and credibility. The term “stockbroker” can be misleading in today’s marketplace because modern brokers don’t limit themselves to trading stocks alone. Instead, as highlighted by Groww, they often facilitate a variety of market transactions, such as:
- Bonds
- Options
- Mutual funds
- Other securities
This broad focus makes them a one-stop shop for many investors. Some stockbrokers also offer additional services, including:
- Retirement planning
- Tax advice
- Automated portfolio rebalancing
Another fundamental aspect is the regulatory environment that stockbrokers operate in. Governments and financial watchdogs worldwide impose strict compliance requirements to safeguard investor interests. These regulatory frameworks ensure that stockbrokers adhere to ethical standards, protect client assets, and maintain transparent business practices.
Whether they work in large brokerage firms or function as independent agents, the constant oversight encourages professionalism, accuracy, and accountability. By grasping these basics, investors can better appreciate the value that stockbrokers bring to the table.
What Does a Stockbroker (share broker) Do?
A stockbroker’s responsibilities extend far beyond simply matching buy and sell orders on a trading platform. While executing trades is undoubtedly central to their job, their role often includes market research, financial analysis, and personalized advisory services.
For instance, a full-service stockbroker may study the financial statements of companies, analyze market trends, and use sophisticated models to forecast future performance. Armed with this information, they can then advise clients on which securities may align best with specific investment goals, risk tolerances, and time horizons.
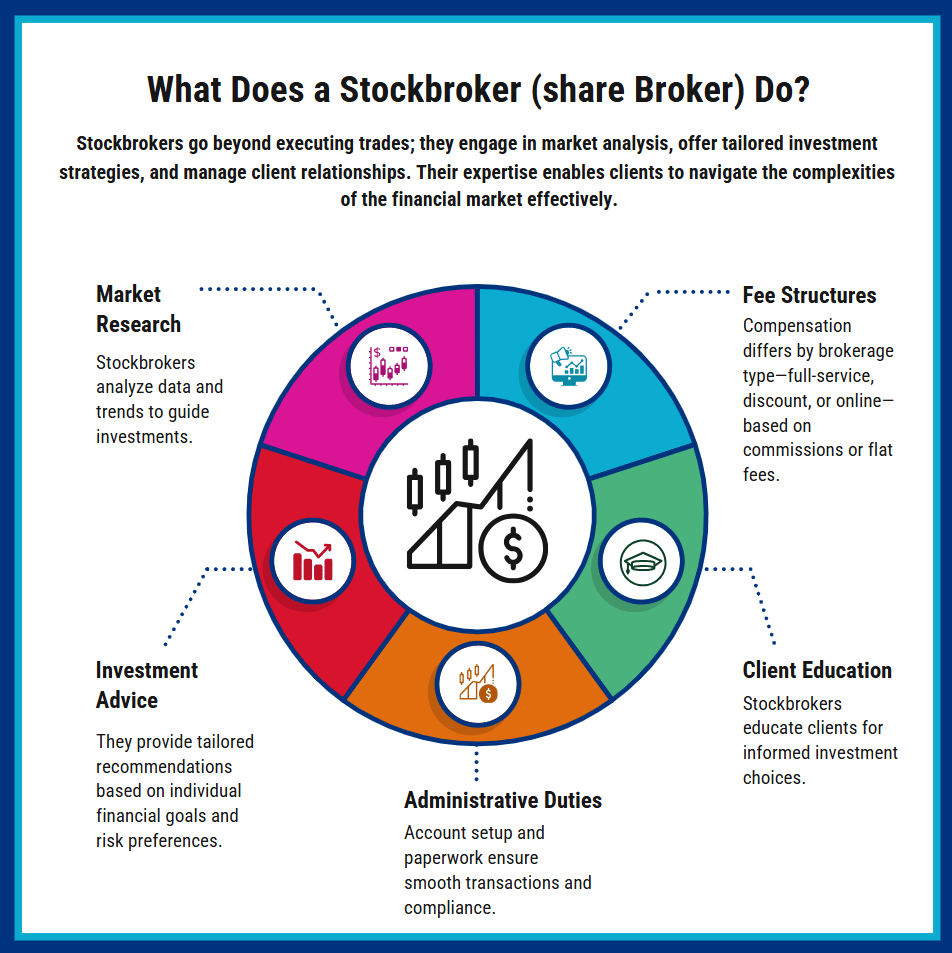
Additionally, stockbrokers manage essential administrative tasks. These range from opening and maintaining client accounts to distributing trade confirmations and account statements. Brokerage firms also keep records of trades, safeguard clients’ funds, and occasionally offer margin accounts for leveraged trading.
Some of these tasks include:
- Opening and maintaining client accounts
- Distributing trade confirmations and account statements
- Keeping records of trades
- Safeguarding clients’ funds
- Occasionally offering margin accounts for leveraged trading
In exchange for these services, they usually charge fees or commissions, which can vary depending on the brokerage model—be it full-service, discount, or online.
Furthermore, stockbrokers play a pivotal role in educating clients. Whether it involves explaining the mechanics of a limit order versus a market order or demystifying more complex instruments like derivatives, a knowledgeable broker can provide clarity. Many brokerages publish newsletters, host webinars, and create training materials to help clients become better-informed investors.
By blending these diverse functions, stockbrokers help individuals and institutions participate in the stock market with greater confidence and efficiency.

Why Are Stockbrokers Important in Financial Markets?
Stockbrokers are essential for maintaining the liquidity and vibrancy of financial markets. When an investor decides to buy shares of a particular company, they generally cannot approach a stock exchange directly. Instead, they rely on brokers who have the authority and infrastructure to execute trades. This channeling process ensures that trades are executed swiftly and accurately.
According to TD Direct Investing, stockbrokers also serve as educators and advisers, helping investors understand market fluctuations and develop strategies to meet their financial objectives.
Beyond trade execution, brokers bring expertise. By analyzing company fundamentals, monitoring macroeconomic indicators, and staying updated on market news, they can offer timely insights that help investors capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks. This is particularly significant in volatile markets, where prices can shift rapidly, and timely execution can make a substantial difference in returns.
Moreover, stockbrokers can mediate complex processes such as IPO subscriptions, rights issues, or corporate actions, freeing investors from the bureaucratic hurdles of direct market involvement.
Finally, stockbrokers uphold integrity within the financial ecosystem. Governed by stringent regulations, they adhere to ethical guidelines designed to protect client interests. This fosters trust and stability, both of which are critical for investor confidence.
With stockbrokers operating as reliable intermediaries, markets can function more efficiently, ensuring that capital flows to businesses that need it, while investors gain the opportunity to grow their wealth.
Key Functions of Stockbrokers
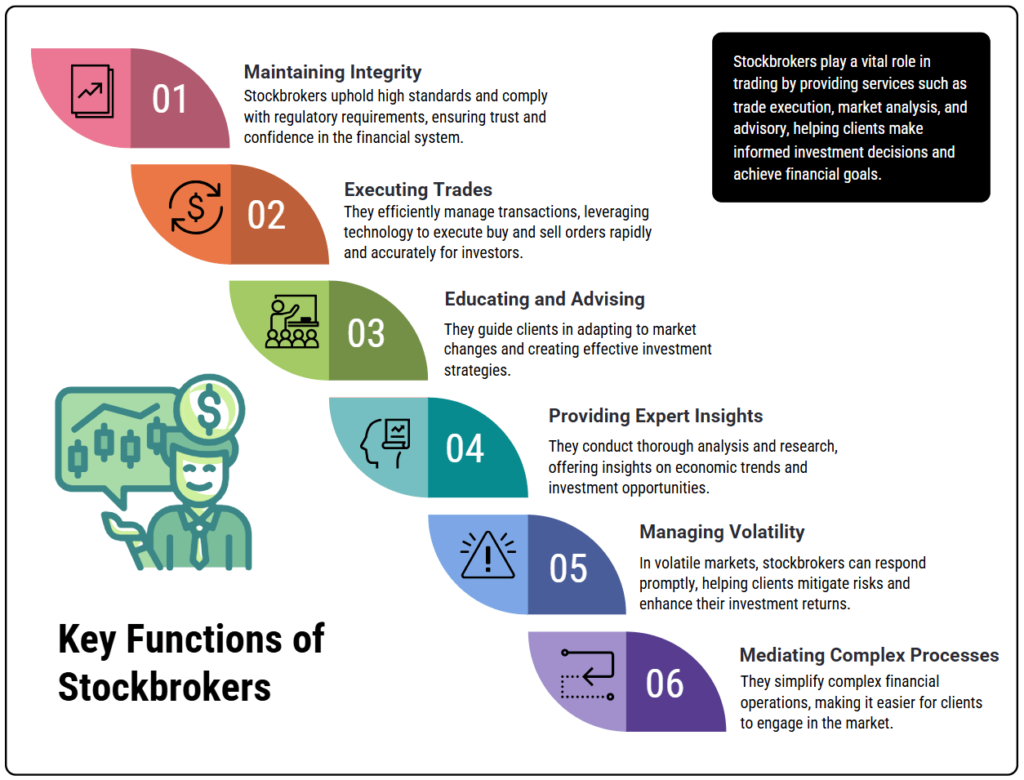
Maintaining Integrity: They operate under strict regulations and ethical guidelines, fostering trust and stability in financial markets.
Executing Trades: They have the authority and infrastructure to quickly and accurately process buy/sell orders.
Educating and Advising: They guide investors on market fluctuations and strategy development.
Providing Expert Insights: They analyze fundamentals, monitor economic indicators, and stay updated on market news.
Managing Volatility: They can act swiftly in rapidly changing markets, which can significantly impact returns.
Mediating Complex Processes: They handle IPO subscriptions, rights issues, and corporate actions, reducing bureaucratic hurdles for investors.
What Is the Role of a Stockbroker?
When we ask, “What is the role of a stockbroker?” we’re focusing on the core functions that shape the investor’s experience in the stock market. At a high level, brokers serve as the conduit between you and the trading floor. They follow your instructions to buy or sell specific securities, taking care of the technicalities and administrative tasks that come with each transaction. Beyond this transactional role, stockbrokers often function as valuable advisors, helping you navigate a marketplace filled with thousands of investment choices.
Stockbrokers (or share broker) may also provide supplementary services like leveraging technology platforms for real-time data analysis. Full-service brokers might have entire research departments dedicated to investigating market movements, sector trends, and economic indicators, translating their insights into actionable advice for their clients. These recommendations can cover anything from short-term trading plays to long-term investment strategies aimed at retirement savings.
Lastly, the role of a stockbroker includes maintaining compliance. They often keep records for audit and regulatory reporting, ensuring that trades follow legal guidelines. By taking responsibility for the technical and legal aspects of buying and selling securities, a stockbroker allows investors to concentrate on strategy and goal-setting.
This comprehensive approach underscores why their services continue to be vital for many types of market participants, from individual retail investors to large institutional clients.
Some key activities of a stockbroker include:
- Serving as a link between investors and the trading floor
- Executing buy and sell orders as instructed by clients
- Providing advisory services on various investment choices
- Leveraging real-time data analysis tools
- Conducting in-depth market, sector, and economic research
- Offering recommendations for both short-term and long-term investment strategies
- Maintaining compliance and thorough record-keeping for audit and regulatory purposes
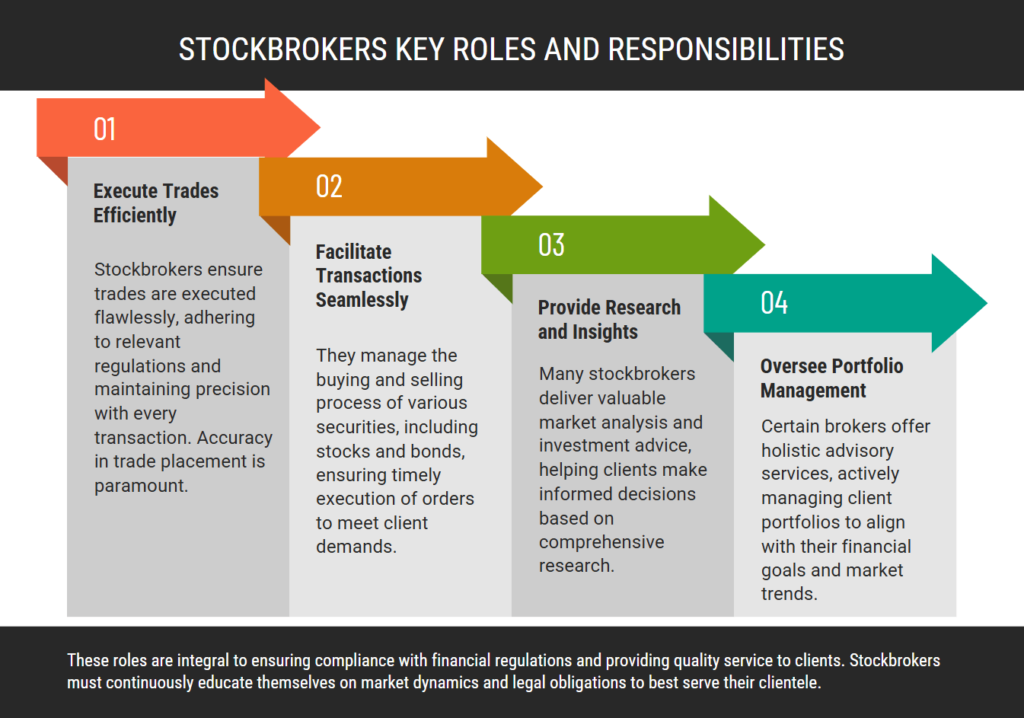
The Primary Responsibilities of a Stockbroker (share broker)
While different brokerage models exist—full-service, discount, or entirely online—they share several core responsibilities that define the profession.
• The first responsibility is trade execution. Whether a client wants to buy a single share or thousands, the broker ensures the order is routed correctly and settled in accordance with market rules. This execution includes timely reporting of trades, so the client knows exactly when and at what price the transactions occurred.
• Another key responsibility involves client consultations. Many investors seek expert advice to help them make informed decisions. A stockbroker typically consults with clients to understand their risk tolerance, financial objectives, and investment timeline. This communication lays the foundation for building or adjusting a portfolio that aligns with the client’s needs. High-touch brokers might conduct periodic reviews, providing market updates and portfolio performance summaries.
• Additionally, stockbrokers play a protective role by adhering to regulatory standards. They must maintain ethical conduct, avoid conflicts of interest, and comply with “know your customer” (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) rules. On top of that, they safeguard client data by implementing robust cybersecurity measures, as highlighted in many industry regulations.
All these responsibilities coalesce to create a professional environment where investors feel secure, informed, and well-served in their quest to grow their wealth.
How Stockbrokers Assist Investors in the Stock Market
Stockbrokers’ main value lies in guiding investors—whether they are novices or seasoned veterans—through the complexities of the financial markets.
For those new to investing, brokers often offer educational resources that cover everything from the basics of stock ownership to the nuances of technical analysis. This guidance can be instrumental in preventing beginners from falling victim to common pitfalls, such as panic selling during a downturn or risking more capital than they can afford to lose.
Seasoned investors might rely on stockbrokers for:
• Advanced analytics
• Exclusive research
• Specialized order types, such as stop-limit orders
According to IG, brokers derive income from various sources, including commissions, spreads, and sometimes margin interest. Understanding these revenue streams helps investors choose a brokerage that offers the right balance of cost-effectiveness and service quality.
A broker’s assistance also extends to portfolio rebalancing. Over time, a portfolio’s original asset allocation can shift due to market fluctuations. Stockbrokers help restore balance by selling overperforming assets and acquiring those that are underrepresented in the portfolio.
This disciplined approach manages risk and maintains alignment with long-term objectives. All these layers of support illustrate why stockbrokers remain a pivotal resource in the investment landscape.
What Is the Role of a Stockbroker (share broker) in the Stock Market?
In the broader context of the stock market, stockbrokers are indispensable players who keep trading activities fluid and efficient. They collect orders from individual and institutional clients and match them with corresponding offers on the market. This fundamental process contributes to market liquidity. It ensures that securities can be bought or sold quickly without significant price disruptions. It’s akin to an engine that keeps the wheels of capital markets turning smoothly.
At the same time, a stockbroker’s role in the stock market extends to providing real-time data and analytics. Platforms provided by modern brokers often feature live price feeds, charting tools, and algorithmic scanners that sift through market data to identify opportunities. By leveraging this technology, brokers are able to offer rapid executions and sophisticated insights, which can be especially important in markets where seconds can make or break a trade.
Finally, the broker also manages after-trade processes. This includes:
• Ensuring that settlements occur properly
• Confirming that shares move from the seller’s account to the buyer’s account
• Ensuring that the corresponding payment is transferred
Any discrepancies or disputes are typically handled by the broker’s support and compliance teams. In essence, a broker’s role is not confined to trade execution alone; it encompasses every phase of the transaction lifecycle, thereby maintaining stability and trust in the financial marketplace.
Facilitating Trades: Connecting Buyers and Sellers
Facilitating trades is arguably the most recognized function of a stockbroker. When you decide to invest in a particular stock, your broker channels your order to the appropriate stock exchange or trading venue. This function goes beyond simply pushing a button. Brokers must ensure the order type—market, limit, stop-loss, or otherwise—is executed at the best possible price. Effective trade facilitation is about accuracy, speed, and cost-efficiency.
Connecting buyers and sellers in real time requires robust technological infrastructure. Many modern brokerage firms operate advanced electronic networks that can handle enormous volumes of trades per second. These high-speed systems reduce latency and slippage, ensuring that the final execution price is as close as possible to the quoted price. For large institutional orders, brokers may utilize algorithms designed to minimize market impact. Often, they break large trades into smaller chunks to avoid drastic price movements.
Once the trade is matched, the broker coordinates the settlement process by:
- Verifying that the buyer has sufficient funds in their account
- Checking that the seller holds the securities to be sold
By acting as an intermediary, the broker minimizes counterparty risk and ensures that both parties fulfill their obligations. This layer of reliability underscores the importance of brokers in maintaining the smooth operation of stock markets worldwide.
Providing Investment Advice and Portfolio Management
Many investors seek more than just trade execution—they also value personalized guidance. Stockbrokers often act as financial advisors, offering tailored recommendations based on a client’s:
- Investment goals
- Risk tolerance
- Time horizon
For example:
- An investor saving for retirement in 30 years might benefit from a portfolio focused on growth-oriented equities.
- A client nearing retirement may prefer income-generating assets, such as dividend stocks or bonds.
Some brokers provide comprehensive portfolio management services, which may include:
- Developing an asset allocation strategy
- Monitoring portfolio performance
- Making periodic adjustments to reflect market changes
A well-structured portfolio typically includes diversification across asset classes and sectors. This approach helps reduce the impact of a downturn in any one area. A stockbroker’s expertise can be instrumental in creating such a balanced and diversified portfolio.
When giving advice, brokers rely on extensive research and analysis. Full-service firms often employ teams of analysts who specialize in various industries or asset classes. These analysts produce detailed research reports that inform the broker’s recommendations.
For investors who lack the time or expertise to conduct their own analysis, a stockbroker’s advice can significantly enhance investment outcomes. Whether you’re seeking:
- Short-term trading tips, or
- A long-term growth strategy
A knowledgeable broker can help you invest with greater confidence.
Ensuring Compliance with Financial Regulations
Compliance with financial regulations is a cornerstone of the stockbroker’s profession. Strict rules govern trading activity to protect investors and ensure fair market conditions. For example:
- Brokers must follow “best execution” practices, which require executing trades on the most favorable terms reasonably available.
- They also have fiduciary duties, meaning they must prioritize their clients’ interests over their own when offering investment advice.
Stockbrokers must also comply with know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. This involves:
- Collecting sufficient information about clients to detect and prevent illegal activities, such as money laundering or terrorist financing.
- Meeting these standards is essential, as failure to do so can result in regulatory penalties and damage to a broker’s reputation.
On the technological front, compliance includes implementing strong cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive client data. Brokers invest in:
- Secure networks and encryption protocols.
- Surveillance systems that monitor trading activities for suspicious behavior.
These efforts help build trust between clients and brokerages, ensuring a level playing field where the focus is on ethical, sound investing. For investors, working with a compliant broker provides reassurance that their money is in safe hands.
Types of Stockbrokers (share broker)
Not all stockbrokers are created equal. The industry has evolved to meet diverse investor needs, offering several types of brokerage services. Whether you’re a new investor seeking guidance or a cost-conscious trader wanting minimal frills, there’s a brokerage model to suit your requirements. Understanding these categories is key to selecting the right fit.
Full-Service Stockbrokers
Full-service brokers offer a comprehensive suite of services, including:
- Executing trades
- Providing in-depth market research
- Offering personalized investment advice
Clients often have access to a dedicated account manager who tailors strategies to their specific goals. This option is ideal for those who value hands-on support and expert guidance.
Discount Stockbrokers
Discount brokers focus on lower commission rates and streamlined services. While they execute trades efficiently, their advisory offerings are limited. This model suits investors who prefer to make their own decisions and prioritize cost savings.
Online Stockbrokers
Online brokers have gained immense popularity due to their digital platforms, which provide:
- User-friendly dashboards
- Educational tools
- Mobile apps for trading on the go
These platforms have lowered the barriers to entry, allowing more people to participate in the stock market.
By weighing the pros and cons of each type, investors can choose the brokerage model that best aligns with their investing style, budget, and objectives.
Full-Service Stockbrokers: Comprehensive Assistance
Full-service stockbrokers are the traditional heavyweights of the brokerage world. They offer a wide range of services designed to address nearly every financial need. From personalized portfolio management to in-depth research reports, they aim to leave no stone unturned.
These brokers typically employ teams of analysts who focus on:
- Company fundamentals
- Industry trends
- Macroeconomic indicators
This results in cutting-edge insights that clients can act upon. For those new to investing or without the time to conduct thorough research, this comprehensive approach can be invaluable.
A standout feature of full-service brokers is personalized attention. Clients often gain direct access to a dedicated advisor. This advisor takes time to understand their:
- Investment goals
- Risk tolerance
- Personal circumstances
This one-on-one relationship fosters trust and ensures that recommendations are tailored to the client’s specific needs. Additionally, many full-service brokers provide:
- Estate planning
- Retirement solutions
- Tax-efficient strategies, especially for high-net-worth individuals.
That said, such extensive services come at a cost. Full-service brokers generally charge higher commissions or fees compared to discount or online brokers.
For investors who:
- Value expert guidance
- Can afford higher costs
The full-service model can be an excellent choice.
However, if you’re fee-sensitive or prefer a hands-on approach to trading, other brokerage options may offer better value. Ultimately, your decision depends on how much personalized support you need and whether professional advice justifies the additional expense.
Discount Stockbrokers: A Budget-Friendly Option
For cost-conscious investors, discount stockbrokers offer an attractive alternative. These brokers focus on enabling trades at lower fees, making them ideal for those who prefer a DIY approach to investing.
Instead of providing in-depth research reports or personalized portfolio advice, discount brokers typically offer simple tools and platforms. This streamlined setup works well for investors confident in their own analysis or those using strategies like passive index investing, where frequent research and advice are unnecessary.
However, the main trade-off with discount brokers is the lack of personalized advisory services. While some may include basic market insights or educational resources, they generally don’t match the one-on-one support offered by full-service firms.
Discount brokers have gained popularity, driven by the rise of low-cost investment options and the availability of financial education online.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Discount Broker
- Cost Savings vs. Support: Evaluate if the reduced fees outweigh the absence of personalized guidance.
- Active Trading Benefits: Frequent traders benefit from lower commissions, which can help maximize profits.
- Beginner Challenges: New investors or those unsure of market dynamics might struggle without professional advice.
Discount brokers offer a budget-friendly way to engage in the stock market. However, they’re best suited for investors comfortable managing their own decisions.
Online Stockbrokers (share broker): The Modern Approach
Online stockbrokers represent the cutting edge of trading today. By leveraging web-based platforms and mobile applications, these brokers enable investors to manage their portfolios anytime, anywhere. The convenience is a significant advantage, allowing users to quickly review market data, execute trades, and receive real-time notifications—all through intuitive interfaces. Many platforms even integrate AI-driven tools that analyze market patterns and provide tailored insights.
The cost structures for online brokers vary widely:
- Commission-Free Trading: Some platforms offer commission-free trading for certain asset classes.
- Alternative Revenue Streams: Brokers often recoup costs through spreads, subscription fees for advanced features, or other charges.
- Additional Fees: According to IG, brokers also generate revenue from margin interest, overnight funding, and ancillary charges.
Understanding the fee schedule is crucial before committing to any platform, as these costs can significantly impact overall returns.
Online brokers often provide educational and support resources, such as:
- Tutorials
- Webinars
- Virtual trading simulators
However, personalized assistance may be limited, as interactions typically occur through digital channels.
For tech-savvy investors who value convenience and are comfortable making independent decisions, online brokers offer a modern, efficient way to invest. These platforms often feature competitive fee structures and robust tools, democratizing access to financial markets for people around the world.
How to Choose the Right Stockbroker
Selecting the right stockbroker (share broker) is a crucial step in your investment journey. The right broker can simplify trading, provide valuable insights, and protect your investments. On the other hand, choosing the wrong one may lead to hidden fees, poor support, and missed opportunities.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Broker:
- Services Offered: Assess the range of services provided. Are they aligned with your needs, such as research tools, portfolio management, or trading platforms?
- Fee Structure: Understand the costs involved, including commissions, account maintenance fees, and hidden charges.
- Track Record: Look into the broker’s experience and reputation in the market.
Determine Your Investment Goals:
- Long-Term Growth: If you’re focused on long-term investing, a full-service broker might be worth the higher cost. Their personalized advice can help build a strong portfolio.
- Short-Term Trading: For frequent trading or self-directed investing, consider a discount or online broker. They’re typically more cost-effective and cater to independent decision-makers.
Importance of Customer Service:
- Personalized attention can be essential, especially if you’re new to investing or value guidance.
- Look for brokers with responsive support, whether through phone, email, or chat.
Assess Reliability and Reputation:
- Read Reviews: Explore online feedback to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Consult Trusted Sources: Check financial websites or forums for professional opinions.
- Verify Credentials: Ensure the broker is licensed and compliant with regulatory authorities. According to Wikipedia, a legitimate broker will always be in good standing.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a broker that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance, ensuring a smoother and more rewarding investment experience.
The Future of Stockbroking
The brokerage industry is evolving rapidly, driven by emerging technologies, changing investor preferences, and regulatory shifts. Modern investors now have more options than ever, thanks to the proliferation of mobile trading apps and zero-commission platforms. This competitive landscape is forcing brokers to innovate continuously, offering features such as:
- Algorithmic trading
- Social investing tools
- Integrated research dashboards
As global financial markets become more interconnected, brokers are also expanding their product range to include international stocks, forex, cryptocurrencies, and more.
Personalization in Brokerage
Personalization is another significant trend shaping the industry. Brokers are leveraging big data and machine learning to provide tailored investment recommendations. For example, AI-driven portfolio management systems can analyze an investor’s:
- Past transactions
- Risk tolerance
- Market sentiment
This analysis enables the generation of highly customized investment suggestions. Such advancements are gradually blurring the lines between traditional full-service brokers and modern robo-advisors, creating hybrid advisory models.
Challenges: Cybersecurity and Compliance
While technological advancements bring opportunities, they also introduce challenges. Brokers face growing concerns related to:
- Cybersecurity: Storing large amounts of sensitive data makes them a prime target for cybercriminals.
- Regulatory compliance: Regulators are increasing oversight to protect consumers, especially as new financial instruments and trading models emerge almost daily.
A Bright Future
Despite these challenges, the future of stockbroking looks promising. Investors can expect more accessible, efficient, and customer-focused offerings, catering to a diverse range of needs and preferences.
Conclusion: Why Stockbrokers Are Vital in Financial Markets
Stockbrokers are essential players in keeping financial markets functioning efficiently. They handle more than just executing trades; they provide vital services such as research, investment advice, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
In today’s rapidly changing financial landscape, understanding what a stockbroker (or share broker) does and how they can assist you is more important than ever. Whether you prefer full-service brokers who guide you through every step of your investment journey or discount and online platforms that offer low-cost, self-directed trading, there’s a stockbroker model tailored to nearly every type of investor.
Stockbrokers play a broader role than just connecting buyers and sellers. They help democratize investing by:
- Ensuring fair and transparent markets
- Adhering to regulatory standards
- Leveraging technology for better trade execution and investment advice
Whether you need personalized portfolio management or a cost-effective trading platform, selecting the right broker can significantly impact your long-term financial success.
As the financial industry evolves, stockbrokers continue to adapt with innovations like:
- Robo-advisors
- Algorithmic trading
- Enhanced digital platforms
Their expertise, combined with these technological advancements, creates a dynamic ecosystem that empowers investors to grow their wealth with confidence and clarity.
Ultimately, a trusted and well-chosen stockbroker (share broker) can be one of your most valuable allies in navigating the complexities of modern finance.
What Is a Stockbroker FAQs
A stockbroker is a licensed individual or firm that facilitates the buying and selling of stocks and other securities on behalf of clients. They serve as intermediaries between investors and the stock market, ensuring trades are executed correctly and in compliance with regulations.
Consider factors such as fee structure, level of service, reliability, and your own investment goals. If you need in-depth advice and research, a full-service broker might suit you. If you prefer lower costs and self-directed investing, a discount or online broker may be a better fit.
Fees can include commissions per trade, account maintenance charges, spreads, margin fees, and sometimes subscription costs for premium services. Make sure to compare fee schedules carefully and look out for any hidden charges like inactivity or withdrawal fees.
Full-service brokers provide comprehensive support, including research, portfolio management, and personalized advice—often at higher costs. Discount brokers focus mainly on trade execution and typically charge lower fees, appealing to more cost-conscious or experienced investors.
In many regions, individual investors are required to place trades through a licensed broker. However, the rise of online and app-based platforms has made the brokerage process more automated. Even so, at the core, a licensed broker or brokerage entity is still handling the trades.
Most brokers earn revenue through commissions on trades or account fees. Others may profit from spreads, margin interest, and additional fees like overnight financing for certain types of trades. Be sure to review a broker’s fee structure to understand all potential costs.
Reputable online brokers typically use secure technology like encryption and two-factor authentication to protect clients’ accounts and information. Always check if the broker is regulated in your jurisdiction and read up on user reviews, security measures, and regulatory filings.
Yes. Transferring an investment account is usually straightforward but may involve paperwork or transfer fees. It’s essential to confirm costs, ensure no trades are pending, and coordinate with both brokerages to make the transition smooth.





