An ECN broker is a financial intermediary that uses an Electronic Communication Network (ECN) to link individual traders directly to major liquidity providers—such as banks, hedge funds, or other traders—without the involvement of a traditional dealing desk. By aggregating price quotes from multiple market participants, an ECN broker provides highly competitive bid and ask prices, transparent trading conditions, and speedy order execution. This structure contrasts with market-making brokers, which often take the opposite side of clients’ trades. ECN brokers aim to offer a more level playing field, making them popular among experienced Forex and CFD traders seeking tighter spreads, direct market access, and more anonymity in trade execution.
What is an ECN Broker? Understanding the Basics
An ECN broker operates on a network that consolidates quotes from multiple liquidity providers. Instead of relying on one internal dealing desk that sets prices, an ECN broker presents real-time market prices aggregated from external sources. This mechanism makes the trading environment more competitive and transparent.
In a typical ECN setup, individual orders are matched with corresponding orders from other participants in the network. For example, a trader looking to sell a currency pair at a certain price can be matched with another trader (or institution) aiming to buy that same currency pair at that price. This matching process is automatic and fast, often yielding lower spreads. However, traders must pay a small commission fee to the broker for facilitating direct access to the interbank markets.
Key Points
- Transparent Pricing: Price quotes come from various top-tier liquidity providers, ensuring accuracy.
- No Dealing Desk: The broker does not create artificial prices or trade against the client’s position.
- Small Commission Fee: Instead of widening spreads, ECN brokers typically charge a commission per trade.
How an ECN Broker Differs from a Dealing Desk Broker
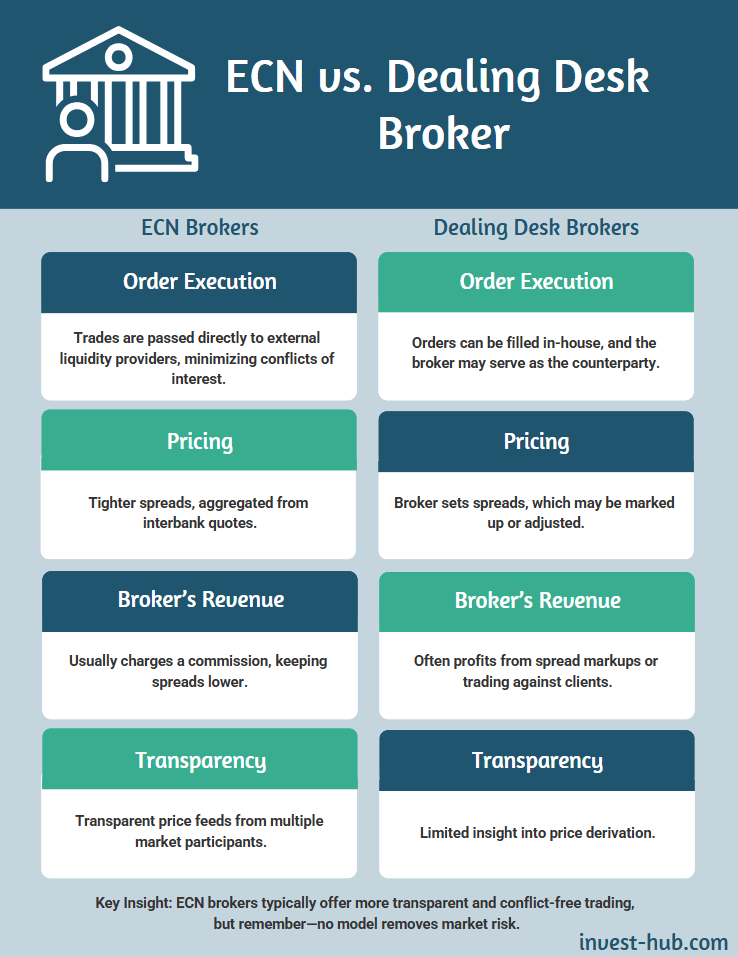
Many newcomers to Forex or CFD trading wonder how an ECN broker stands apart from a dealing desk (or market-maker) broker. Traditional dealing desk brokers often derive their profits from the spread itself or by taking the opposing side of traders’ orders. In contrast, an ECN broker matches each client’s order with an external participant, eliminating a direct conflict of interest.
Core Differences
- Order Execution
- Dealing Desk: Trades can be processed in-house, and the broker may act as a counterparty.
- ECN Broker: Trades are routed to external liquidity providers through an electronic hub.
- Dealing Desk: Trades can be processed in-house, and the broker may act as a counterparty.
- Pricing
- Dealing Desk: The broker sets the spread, which can be marked up or variable based on in-house decisions.
- ECN Broker: Spreads are derived from interbank quotes, generally resulting in tighter spreads.
- Dealing Desk: The broker sets the spread, which can be marked up or variable based on in-house decisions.
- Broker’s Revenue
- Dealing Desk: Profits often come from the spread markup or opposing client trades.
- ECN Broker: Typically earns through a fixed or volume-based commission while keeping the spreads low.
- Dealing Desk: Profits often come from the spread markup or opposing client trades.
- Transparency
- Dealing Desk: Limited visibility into how prices are derived.
- ECN Broker: Price aggregation is transparent, coming directly from numerous market participants.
- Dealing Desk: Limited visibility into how prices are derived.
Because an ECN broker has no incentive to trade against clients, many experienced market participants believe this model provides a fairer environment. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that transparency and better pricing do not guarantee profitable trading results—market risk remains.
Advantages of Using an ECN Broker
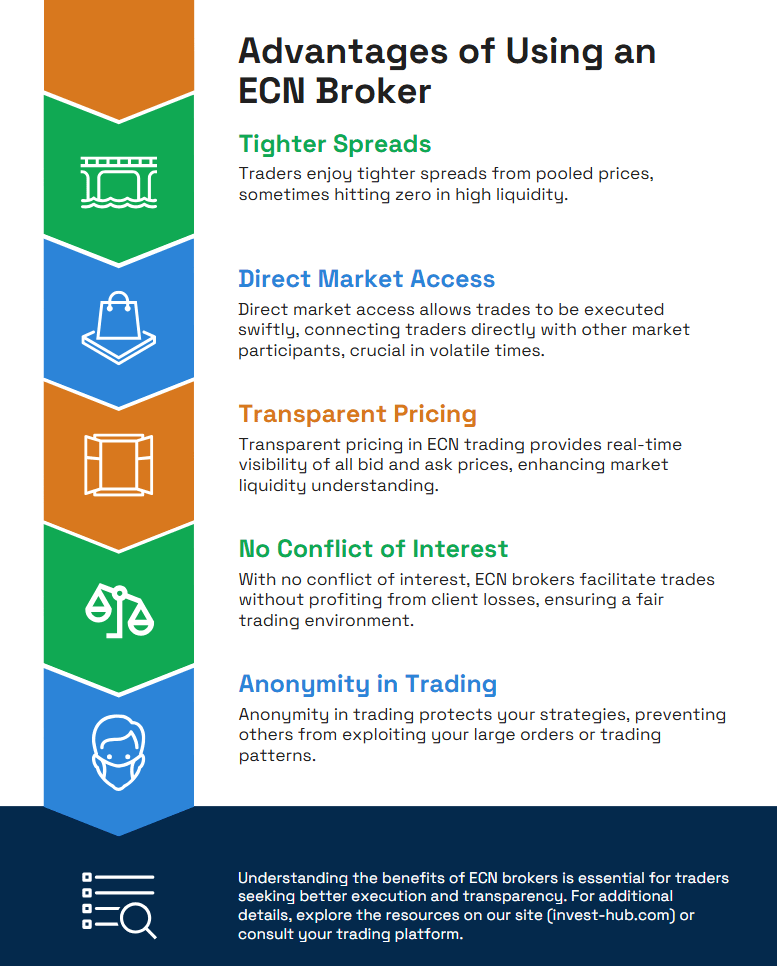
Traders who prioritize fair execution, tighter spreads, and market transparency often gravitate toward ECN brokers. Below are some of the key advantages that attract both retail and institutional traders:
- Tighter Spreads
Since prices are pooled from numerous liquidity providers, spreads can be very low—sometimes as low as zero during periods of heightened market liquidity. - Direct Market Access
With an ECN, your trades go directly to other traders or financial institutions. This structure often results in real-time, rapid trade execution, which can be crucial during volatile market conditions. - Transparent Pricing
An ECN broker typically posts all available bid and ask prices in real time, allowing you to see the full depth of market liquidity. - No Conflict of Interest
The broker’s role is purely to connect buyers and sellers, collecting a commission for enabling the transaction. This approach reduces the likelihood that the broker is profiting from client losses. - Anonymity in Trading
Many ECN brokers offer anonymous trading, which can prevent other market participants from gauging large orders or using your trading activity against you.
Comparing to Other Models
- Straight Through Processing (STP): Similar to ECN, but the broker might still source quotes from a limited pool of liquidity providers.
- Market Makers: Create their own liquidity and often widen spreads, which can be less favorable to traders who prioritize minimal costs.
Potential Drawbacks of an ECN Broker
While an ECN broker offers numerous benefits, no brokerage model is perfect. Here are some potential drawbacks to keep in mind:
- Commission Costs
Because spreads tend to be very low, commissions can be higher than with market-maker or STP-only brokers. Active traders must carefully calculate the net cost of tighter spreads plus commission charges. - Higher Minimum Deposits
Certain ECN brokers require higher initial deposits to maintain liquidity relationships with top-tier providers. This requirement can deter beginners or small-scale traders. - Market Volatility
In extremely volatile markets or during low liquidity periods (like weekends or holidays), spreads can widen unexpectedly—though such changes are market-driven rather than broker-driven. - Platform Complexity
ECN trading platforms can be more sophisticated, offering direct-order routing and market depth analysis. This complexity might overwhelm novices unfamiliar with advanced trading tools.
Traders should weigh these costs and challenges against the advantages of direct market access. For many serious traders, the benefits of genuine price transparency outweigh the associated costs. You can read more about practical ECN trading tips in FXTM Education.
Key Features That Define a Quality ECN Broker
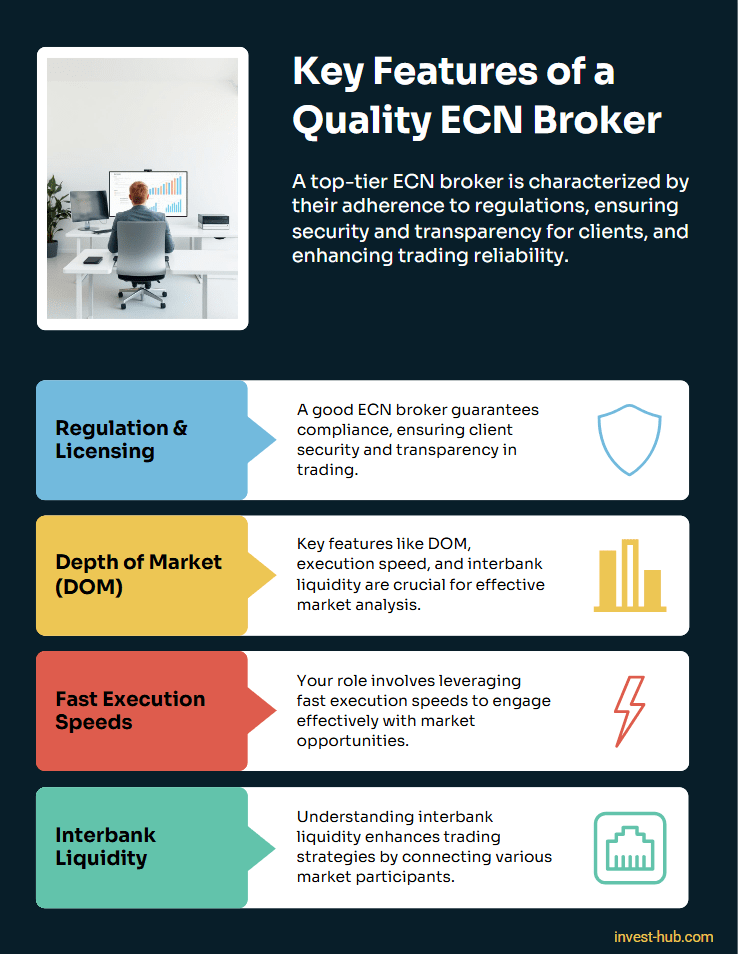
Selecting the right ECN broker can significantly influence your trading experience. Beyond low spreads and direct access, there are several other features to look for.
Regulation and Licensing
A reputable ECN broker is licensed and regulated by recognized financial authorities. Well-known regulatory bodies often impose strict rules designed to protect traders’ interests and ensure transparent business practices. Whether you’re a Forex, CFD, or cryptocurrency trader, make sure to confirm the broker’s license with the appropriate agency. You can check a broker’s license with multiple sources like FCA.
Depth of Market (DOM)
One of the hallmarks of a genuine ECN platform is the ability to see Depth of Market (DOM). This feature displays the available liquidity at varying price levels, giving you insight into where large orders reside. Access to DOM can improve your decision-making about entry and exit points, particularly in fast-moving markets.
Fast Execution Speeds
In an ECN environment, you typically enjoy rapid execution due to direct matching of buyer and seller orders. However, technology infrastructure also matters. A broker employing stable servers and advanced matching engines can handle high trading volumes with minimal slippage.
Interbank Liquidity
Because an ECN broker aggregates quotes from numerous liquidity providers (often banks, hedge funds, and other financial institutions), traders gain access to the interbank market. This translates to highly competitive pricing and a more seamless trading experience.
Comparing an ECN Broker to an STP Broker
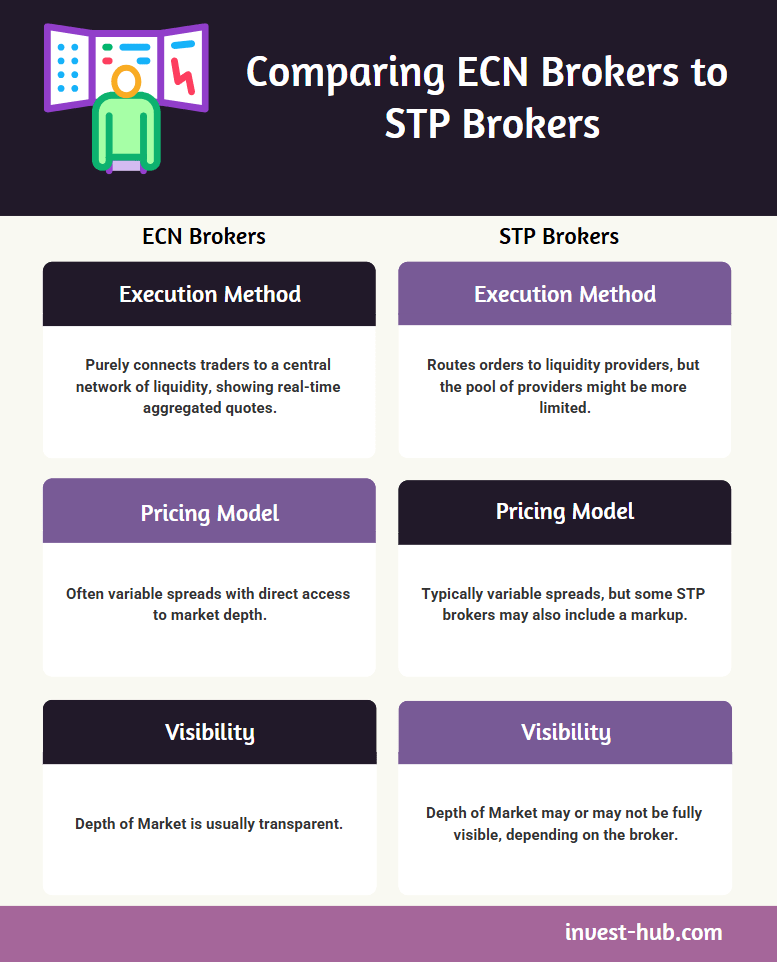
Although ECN and STP (Straight Through Processing) brokers share similarities, the slight nuances can impact your trading approach.
- Execution Method
- ECN: Purely connects traders to a central network of liquidity, showing real-time aggregated quotes.
- STP: Routes orders to liquidity providers, but the pool of providers might be more limited.
- ECN: Purely connects traders to a central network of liquidity, showing real-time aggregated quotes.
- Pricing Model
- ECN: Often variable spreads with direct access to market depth.
- STP: Typically variable spreads, but some STP brokers may also include a markup.
- ECN: Often variable spreads with direct access to market depth.
- Visibility
- ECN: Depth of Market is usually transparent.
- STP: Depth of Market may or may not be fully visible, depending on the broker.
- ECN: Depth of Market is usually transparent.
In practice, many brokers blend STP and ECN elements. True ECN brokers give a more transparent, direct route to interbank liquidity, whereas STP brokers might simplify the process but offer slightly less visibility. You can read more about ECN vs. STP in Admirals Academy.
How to Choose the Right ECN Broker
Selecting an ECN broker is a pivotal choice that can shape your trading success. Here are some guidelines to help you weigh your options:
- Check Regulation
- Ensure the broker is regulated by reputable agencies. Licensing details should be transparent on their official website or in company documents.
- Ensure the broker is regulated by reputable agencies. Licensing details should be transparent on their official website or in company documents.
- Examine Trading Costs
- Look beyond just spreads. Factor in commission fees, deposit and withdrawal fees, and any potential inactivity charges.
- Look beyond just spreads. Factor in commission fees, deposit and withdrawal fees, and any potential inactivity charges.
- Assess Platform Features
- Verify if the broker’s platform supports DOM, advanced charting, algorithmic trading, and other relevant tools. If you plan to automate trades, confirm that the platform integrates well with your preferred strategy.
- Verify if the broker’s platform supports DOM, advanced charting, algorithmic trading, and other relevant tools. If you plan to automate trades, confirm that the platform integrates well with your preferred strategy.
- Review Execution Speeds
- Slow trade execution can erode profits, especially for scalpers. Some brokers publish average execution speeds or slippage data.
- Slow trade execution can erode profits, especially for scalpers. Some brokers publish average execution speeds or slippage data.
- Customer Service
- Reliable, accessible, and knowledgeable customer support is crucial, especially if you face technical issues or have questions about your account.
- Reliable, accessible, and knowledgeable customer support is crucial, especially if you face technical issues or have questions about your account.
- Research Reputation
- Use trader forums, social media groups, and independent review sites to glean insights about the broker’s track record, reliability, and client satisfaction.
- Use trader forums, social media groups, and independent review sites to glean insights about the broker’s track record, reliability, and client satisfaction.
Tip:
Start with a demo account, if available, to test the broker’s platform and execution conditions before committing real funds.
Real-World Application of ECN Brokers
In practical terms, an ECN broker caters to both institutional and retail traders who seek direct market access. For high-volume trading strategies, such as scalping or day trading, these brokers can be particularly advantageous because of lower spreads. Professional traders value the transparent execution model, while less experienced traders might appreciate the objective, level playing field—though they also need to be mindful of commissions and potential learning curves.
Institutions like hedge funds or large trading firms can benefit from ECN broker services for improved execution in Forex, commodities, or even cryptocurrency pairs. The synergy created by matching large buy and sell orders in a shared liquidity pool can make for less slippage when executing major trades.
Conclusion
In summary, What is an ECN broker? It is a brokerage model that prioritizes transparency, fairness, and direct market access by linking traders to a broad range of liquidity providers through an Electronic Communication Network. This setup can result in tighter spreads, real-time market depth, and minimal broker interference in trade execution. While the commission costs and higher deposit requirements may deter some newcomers, many experienced traders find the advantages—such as improved pricing, transparency, and the absence of a dealing desk—well worth the investment. Before you select an ECN broker, do your due diligence on regulatory status, trading platform features, and overall reputation. By choosing wisely, you can harness the benefits of direct interbank access for a potentially more rewarding trading experience.
Call to Action: Ready to explore the advantages of ECN trading? Research a few reputable brokers, compare their fee structures and tools, and consider starting with a demo account to see how the technology enhances your trading strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes, but it may come with a steeper learning curve due to more advanced platforms and commission-based structures. Beginners should start with a demo account to understand ECN features before risking real capital.
ECN brokers aggregate quotes from various liquidity providers, often resulting in extremely low or zero spreads. To cover operational costs and remain profitable, they typically charge a transparent commission per trade.
Look for evidence of direct interbank liquidity access, real market depth (DOM), transparent pricing, and an explicit commission model. Reputable ECN brokers also openly disclose their network relationships and operating structure.
Often, yes. By linking multiple buyers and sellers directly, ECN brokers can offer rapid trade matching. However, technology infrastructure and server stability also play significant roles in overall execution speed.
Many scalpers prefer ECN brokers because of tighter spreads and fast execution. Always verify that the broker allows high-frequency trading strategies and does not have specific restrictions on scalping.
Minimum deposit requirements vary. Some brokers may cater to retail clients with lower deposit thresholds, while others focus on professional traders requiring higher initial capital.





