A common question for new investors is: What is a broker in the share market? In simple terms, a broker acts as a gateway between you and the stock exchange, enabling you to buy and sell shares with ease. However, the role of a broker extends far beyond simple trade execution. They provide critical insights, guidance, and support that can make a significant difference in your trading success.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about brokers in the share market—from their fundamental responsibilities and types to how they earn money and how you can even become one. Whether you are a seasoned trader or a curious beginner, understanding brokers is crucial to navigating the world of investing confidently.
Introduction: Understanding Brokers in the Share Market
Definition and Basics
The share market, also known as the stock market or equity market, is a platform where stocks (shares of publicly listed companies) are issued, bought, and sold.
A broker in the share market is a licensed intermediary who facilitates the buying and selling of securities on behalf of investors. Brokers may operate as individuals or as part of a brokerage firm. They play a critical role in ensuring smooth transactions by offering you access to the marketplace, executing trades under your instruction, and sometimes even providing portfolio management support.
Brokers must register with regulatory bodies—such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in India or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) in the United States—to legally offer their services. This regulation serves as a protective measure for investors.
Brokers can vary widely in the services they provide: some strictly execute trades, while others also offer financial advice, research tools, and in-depth market analyses.
The most basic function of a stockbroker is to serve as a channel between you and the exchanges—like the National Stock Exchange (NSE) or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) in India.
Today, most brokerage services are available online, making trading more accessible than ever. Nevertheless, each broker type comes with its own features, fee structures, and advantages, which we will explore in depth throughout this guide.
Why You Need a Broker
According to IG, You may wonder why you cannot simply bypass a broker and trade directly on the stock exchange. The primary reason is regulatory compliance: only authorized members can directly transact on stock exchanges. A broker has the necessary legal authority and infrastructure to execute trades. This infrastructure covers everything from secure transaction systems to the compliance mechanisms that safeguard your investments. If you need more information about IG broker, you can read our IG Broker Review 2025.
Moreover, brokers offer resources and insights that can be invaluable, especially for newcomers. Many brokerage platforms provide educational tools, including video tutorials, market analyses, and even one-on-one advisory services, depending on your account type.
A reliable broker will help you minimize risks by offering well-researched advice, guiding you on compliance requirements, and assisting you in formulating a well-rounded investment strategy.
Having a trusted broker can ease your transition into the share market, reduce stress, and help you avoid common pitfalls like emotional decision-making or lack of diversification. Whether you’re a small retail investor or an institutional player, the support of a broker can be a game-changer in achieving your financial goals.
What Is the Role of a Broker in the Share Market?
According to Angelone, the role of a broker in the share market is multifaceted. Beyond simply executing trades, brokers provide a spectrum of services aimed at helping you navigate complex market conditions. Let’s break down their primary responsibilities to understand how they serve investors.
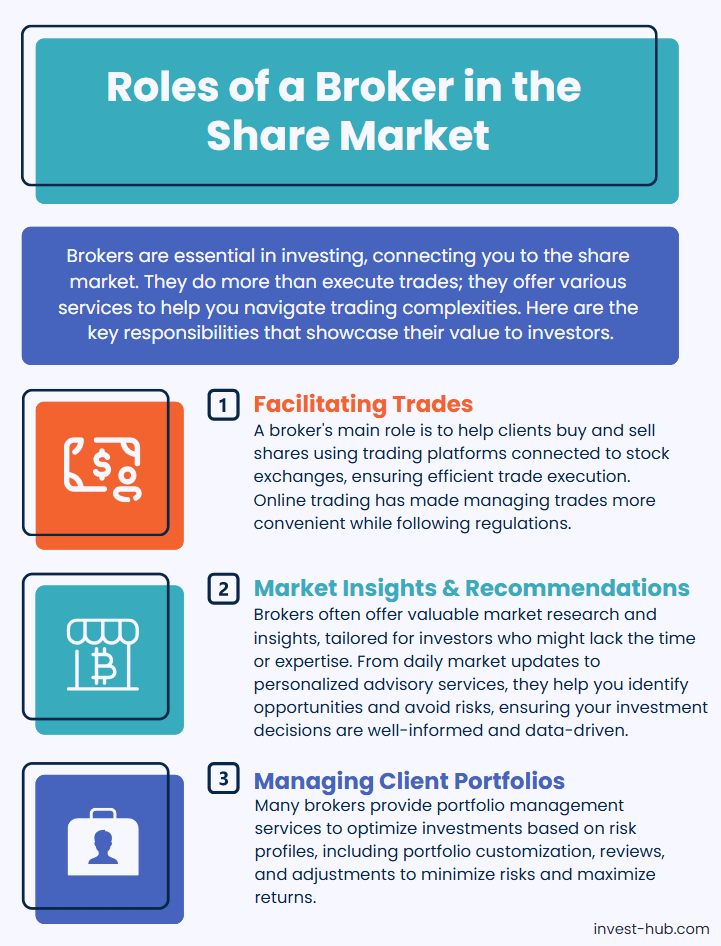
Facilitating Trades
A broker’s foremost responsibility is to facilitate the purchase and sale of shares on behalf of clients. To do this effectively, brokers maintain specialized trading platforms that connect directly to stock exchanges. When you place an order—be it a market order, limit order, or any other type—the broker’s systems route this request to the exchange. Once your order is matched with a suitable counterparty, it is executed.
This seamless process has become even more streamlined with online trading platforms, allowing you to place orders from your smartphone or computer. Brokers also ensure that every transaction complies with regulations. They keep a detailed record of trades, manage settlement processes, and oversee fund transfers to and from your trading account.
In addition to direct facilitation, brokers can offer value-added services like automated trading alerts, advanced charting tools, and watchlists. These tools help you stay updated with real-time market data, ensuring you make informed decisions. In essence, the broker is the linchpin that connects you, the investor, to the massive infrastructure of the share market, enabling you to buy and sell shares with just a few clicks.
Providing Market Insights and Recommendations
Many brokers offer market research and recommendations, which can be especially beneficial for investors who may not have the time or expertise to conduct extensive analysis. Full-service brokers, in particular, often have dedicated research teams that provide daily market updates, technical analysis, and fundamental reports on various companies and sectors.
Even discount and online brokers may provide some level of insight, such as top-moving stocks of the day, market news alerts, or risk management tips. These insights can help investors identify lucrative opportunities or avoid potential pitfalls.
Additionally, a broker may offer personalized advisory services, where an analyst or financial advisor collaborates with you to develop a custom investment strategy aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By combining their market expertise with real-time data, brokers effectively bridge the knowledge gap for investors. This guidance can be crucial during volatile market conditions, helping you maintain discipline and make decisions rooted in data rather than emotion.
Managing Client Portfolios
Beyond trade execution and advisory, some brokers also provide portfolio management services. This can range from basic rebalancing suggestions to comprehensive portfolio overhauls, depending on your risk profile and investment horizons. A good portfolio management service will consider factors such as diversification, asset allocation, and periodic monitoring to help you achieve optimal returns.
Portfolio management offerings can be highly customized. Institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals may opt for bespoke portfolios managed by a dedicated broker or a team of financial experts. Retail investors, on the other hand, can take advantage of model portfolios, automated investing tools, or robo-advisors integrated into the broker’s platform.
By managing a client’s portfolio, a broker not only aims to maximize returns but also works on minimizing risk through strategic asset allocation. Regular portfolio reviews, performance reporting, and timely adjustments are all part of this comprehensive service. Ultimately, this makes the broker an essential partner for those who want an expert eye on their investments without having to handle the complexities of the market themselves.
Types of Broker in Share Market
Brokers come in various shapes and sizes, offering different levels of service, fee structures, and technological platforms. Understanding these distinctions is vital for selecting the best fit for your trading style and investment objectives.
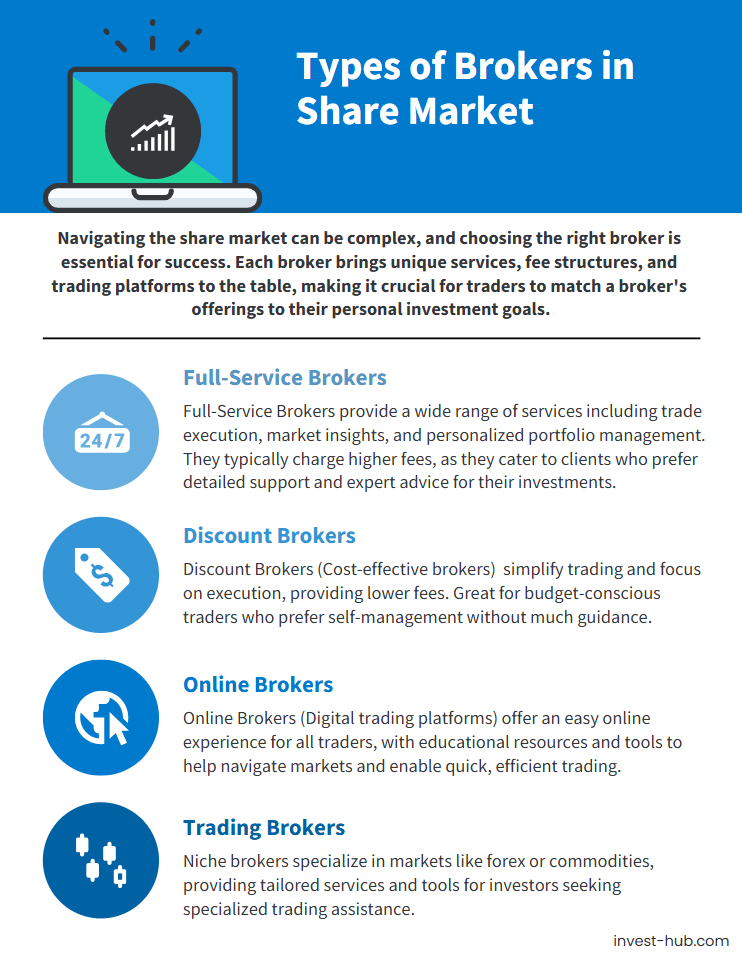
Full-Service Brokers
Full-service brokers are often large brokerage firms that provide end-to-end solutions. Full-service brokers typically offer trade execution, in-depth research reports, personalized advice, portfolio management, and additional perks like access to exclusive initial public offerings (IPOs) or premium market data.
These brokers often come with higher brokerage fees or commissions, given the extensive support and human advisory components. They generally cater to both individual and institutional investors who value professional guidance and are willing to pay a premium for it. Services from these brokers may include one-on-one sessions with market experts, detailed investment planning, and even tax-related guidance. If you’re a new investor seeking hands-on support or a busy professional looking for a trusted team to handle your investment decisions, a full-service broker could be your best bet.
Discount Brokers
Discount brokers focus primarily on trade execution, offering minimal additional services like research or advisory. Their main selling point is lower brokerage fees, which can save active traders or those on a tight budget a substantial amount of money over time. Discount brokers have surged in popularity with the advent of online trading, as they attract cost-conscious investors who are comfortable conducting their own research.
Though these brokers may provide fewer bells and whistles, they generally offer user-friendly platforms complete with basic charting tools and order types. This stripped-down approach allows you to take charge of your investment decisions while keeping transaction costs low. It’s an excellent option for experienced traders who rely heavily on their own strategies and have less need for personalized advisory services.
Online Brokers
While discount brokers frequently operate online, the term “online brokers” can encompass a broader range of platforms, including app-based trading services and robo-advisors. These brokers leverage technology to provide a seamless trading experience, often with intuitive interfaces that cater to users of all experience levels. Many online brokers offer educational content, customizable dashboards, and real-time market updates.
In many ways, the lines between “discount” and “online” brokers have become blurred, as most brokerages now offer a combination of low fees and robust online features. That said, each platform has unique strengths. Some excel in stock screening and advanced analytics, while others focus on social trading features or simplified user experiences for beginners. The convenience, speed, and cost-effectiveness of online brokers make them a top choice for modern-day investors who value autonomy and control over their trades.
Other Specialized Broker Categories
In addition to the most commonly discussed categories, there are specialized brokers that cater to specific market segments or instruments. For instance, there are futures and options brokers who focus on derivatives, forex brokers who specialize in currency trading, and commodity brokers for trading in commodities like gold or crude oil. Each specialized broker offers tools and services tailored to their niche.
There are also institutional brokers that handle large orders for mutual funds, insurance companies, and hedge funds. These brokers often use advanced trading algorithms to mitigate market impact when placing massive orders. Then you have boutique brokerage firms that provide specialized services for high-net-worth individuals. Their offerings may include in-depth portfolio restructuring, estate planning, or philanthropic investment guidance.
The key takeaway is that the term “broker” encompasses a vast range of service models. By understanding these categories, you can more precisely pinpoint which type of broker aligns with your trading goals, risk tolerance, and level of involvement you wish to have in day-to-day market activities.
What Is a Sub Broker in the Share Market?
Another term that often arises when discussing brokerage services is the “sub broker.” A sub-broker acts as an agent who works under a primary broker, offering brokerage services on behalf of that larger entity. Sub-brokers do not have direct access to the stock exchange; instead, they channel trades through their affiliated broker.

Key Functions of a Sub Broker
Sub-brokers perform many tasks similar to those of a main broker, such as handling client inquiries, facilitating trade orders, and offering basic market insights. However, their scope of operation is typically more localized. They often focus on building relationships with retail clients in specific regions or niches, thus expanding the reach of the main brokerage firm.
In addition, sub-brokers often serve as the first point of contact for many investors who might be new to the market. They guide these clients through the account-opening process, instruct them on trading platform usage, and may also offer basic advisory services. Sub-brokers earn commissions on trades executed via their channel. This commission is shared between the sub-broker and the main broker, as outlined by licensing agreements and regulations.
For investors, the advantage of working with a sub-broker can be more personalized attention and localized services. On the flip side, the range of services they offer may be somewhat limited compared to full-service or discount brokers who operate on a larger scale. Still, sub-brokers serve a vital role in expanding market participation and offering hands-on support to newer or regionally focused investors.
Difference Between Broker and Sub-Broker in Share Market
The primary difference between a broker and a sub-broker lies in their regulatory status and direct market access. A broker holds a license from the relevant stock exchange authorities, enabling direct trade execution. A sub-broker, however, functions under a broker’s license and cannot place trades independently on the exchange.
While both can assist with buying and selling shares, offering guidance, and helping investors manage their portfolios, the broker generally provides a broader set of services and has a more robust infrastructure. Sub-brokers, in contrast, often operate at a more grassroots level, focusing on client acquisition and relationship management.
This division of responsibilities can be beneficial for both parties. Brokers can expand their customer reach without having to invest in a physical presence everywhere, while sub-brokers benefit from the backing of a reputed entity. From an investor’s perspective, whether you choose to work directly with a broker or via a sub-broker may come down to convenience, cost, and the level of personalized attention you desire.
How to Become Broker in Share Market

Becoming a share market broker can be a fulfilling career for those passionate about stock trading, finance, and sales. However, it requires specific educational qualifications, licenses, and skill sets. Here’s an overview of the steps involved:
Educational Qualifications and Licensing
- Education: A bachelor’s degree in finance, business administration, or a related field is commonly required. However, individuals with strong numerical skills and market awareness from other educational backgrounds can also succeed.
- Licensing: To become a broker, you need to register with regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and pass certification exams (e.g., NISM exams) that test your knowledge of market regulations and ethical practices.
Steps to Begin Your Career
- Join a Brokerage Firm: Gain hands-on experience in trading, client interaction, and market data analysis.
- Build a Client Base: Strong communication and financial literacy are essential for explaining trends and strategies to clients.
- Advance Your Career: Specialize in roles like equity research analyst, portfolio manager, or start your own brokerage.
Key Skills for Success
- Analytical Skills: Understand market trends, corporate fundamentals, and macroeconomic factors.
- Interpersonal Skills: Build trust with clients through empathy and negotiation.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Stay updated on market regulations and compliance.
- Time Management: Handle multiple client portfolios in the fast-paced stock market.
- Technological Proficiency: Leverage online trading platforms, analytics tools, and emerging technologies like AI for better service delivery.
Success as a broker requires a mix of technical expertise, client relationship management, and adaptability to evolving market and technological trends.
Can I Invest in the Share Market Without a Broker?
The advent of technology and changing regulations has led many to wonder if they can invest in the share market without a traditional broker. While certain avenues exist for direct stock ownership or alternative investments, it’s important to consider the pros and cons before proceeding on your own.
Potential Options for Self-Investing
One way to bypass a traditional broker is by investing in direct stock purchase plans (DSPPs). Some companies allow individuals to buy shares directly from the firm without a broker, although these opportunities can be limited and may come with specific terms. Another option is investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds through fund houses that enable direct purchases. However, even this typically requires at least a demat account and sometimes a trading account, which are often accessed via a brokerage platform.
Another evolving avenue is cryptocurrency markets. Many crypto exchanges operate somewhat like brokerages but with fewer regulatory constraints, offering direct transactions in digital assets. Still, for traditional share market investing, it’s generally more straightforward—and often more secure—to use a broker or a recognized trading platform.
Pros and Cons of Investing Without a Broker
The main advantage of investing without a broker is saving on brokerage fees and commissions. If you’re an investor who prefers a long-term buy-and-hold strategy, these savings can add up over time. Additionally, bypassing a broker can offer more control and autonomy, eliminating any external influences on your investment decisions.
On the downside, you lose access to a broker’s market insights, customer support, and advanced trading tools. According to IG, brokers earn money primarily through commissions, spreads, or platform fees—but in return, they provide valuable services like research, portfolio tracking, and streamlined trade executions. If you invest without a broker, you assume the full burden of research, technical analysis, and risk management. This can be especially challenging for new investors who might not have the necessary expertise.
Ultimately, whether you should invest without a broker hinges on your experience level, risk tolerance, and how comfortable you are managing all aspects of the investment process independently.
Which Is the Best Broker in the Share Market?
Selecting the “best” broker in the share market isn’t a one-size-fits-all proposition. Different traders and investors have varying goals, trading frequencies, and budgetary constraints. The best broker for you is the one that aligns most closely with your specific needs, offering a balance of affordability, reliability, and value-added services.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Broker
When evaluating brokers, fees and commissions often top the list of considerations. Low brokerage costs can significantly impact your overall returns, especially if you are an active trader. Full-service brokers typically charge higher fees but compensate with premium services, including personalized advisory, research, and portfolio management.
Next comes platform usability. A feature-rich, user-friendly interface can greatly enhance your trading experience. Look for easy navigation, real-time data, advanced charting, and customization options that suit your strategy. Regulatory compliance and reputation are also crucial; always choose a broker that’s well-regulated and has a strong track record of customer satisfaction. Checking online reviews, consulting industry reports, and getting referrals from experienced traders can provide additional peace of mind.
Customer service is another pivotal factor. You’ll want a broker that offers responsive support channels—be it via phone, email, or live chat—so you can resolve queries quickly. Lastly, evaluate any additional perks, like educational resources, rewards programs, or advanced research tools, which can substantially enhance your trading and investment journey.
Comparing Top Brokers in the Market
The market is filled with both well-established and emerging brokerage firms. Some popular names in the Indian market often include Zerodha, Groww, Angel One, ICICI Direct, and Upstox, each offering unique advantages. In other countries, different brokers may be more prominent.. For instance:
- Zerodha: Known for its low brokerage model and technologically advanced platform, making it a favorite among active traders.
- Groww: Focuses on user-friendly interfaces and straightforward investment processes, ideal for beginners.
- Angel One: Provides a balance of decent brokerage rates and extensive research tools.
- ICICI Direct: A full-service broker with in-depth advisory but higher brokerage fees.
- Upstox: Competitive pricing and a feature-rich mobile app, appealing to budget-conscious traders.
Each broker distinguishes itself through its pricing structure, platform features, and service quality. Reviewing your personal trading habits—like your average holding period, the number of trades, and the type of securities you focus on—can help you make a more informed choice. Ultimately, “the best” broker will be one that optimally aligns with your trading style, offers robust support, and gives you confidence as you navigate the share market.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
In exploring what a broker is in the share market, we’ve uncovered how brokers serve as indispensable links between investors and the stock exchanges. They provide essential services, from trade execution to portfolio management and advanced advisory. Knowing the role of a broker can help you appreciate why they charge certain fees and what you get in return. We’ve also broken down various categories of brokers—full-service, discount, online, and specialized—each catering to different segments of the investing population.
We delved into the concept of sub-brokers, who extend brokerage services under the umbrella of a primary broker, offering more localized and personalized service. For those aspiring to enter the brokerage field, understanding educational requirements, licensing, and key skill sets is crucial. We even examined investing without a broker, looking at both the freedom it offers and the risks it entails.
Finally, we discussed how to choose the best broker, emphasizing considerations like cost structure, regulatory compliance, and platform features. Ultimately, your choice should align with your investment goals, experience level, and risk tolerance.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
The share market can be a world of opportunity—but also of significant risk. A well-chosen broker can guide you through market complexities, providing the support and tools needed to make informed decisions. After all, understanding what is broker in share market is just the first step; actively leveraging your broker’s resources can help unlock your full potential as an investor or trader.
As next steps, consider your personal investment objectives and risk profile to determine which brokerage model (full-service, discount, or online) aligns best with your strategy. Research and compare at least three brokers in detail—examining their fee structures, platform usability, and customer service. And if you ever plan to advance into the brokerage profession, begin by exploring educational opportunities and regulatory guidelines in your region. Whether you’re a novice investor or an aspiring broker, knowledge is your most powerful asset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About What Is a Broker in the Share Market?
Brokers typically earn money through brokerage fees, commissions per transaction, spreads (in the case of certain forex or CFD trades), and, in some cases, account maintenance fees or margin interest. Brokers can also generate revenue from activities like order flow payment or premium services for advanced research tools.
Yes, online brokers are generally safe if they are well-regulated by recognized financial authorities. Always check for licenses (e.g., SEBI in India, FINRA in the U.S.) and user reviews before signing up. Secure trading platforms employ encryption and multi-factor authentication to safeguard your personal and financial data.
Most brokers allow you to switch services whenever you choose. However, you may incur transfer or account closure fees. It’s wise to weigh these costs against any potential benefits of moving to a new broker with better features or lower commissions.
If you value direct market access, comprehensive research tools, and a broad range of services, working with a primary broker might be the best option. If you prefer personalized attention or have a local advisor you trust, a sub broker affiliated with a reputable main broker can be a good choice.
Always review the broker’s fee schedule carefully. Potential hidden charges can include platform fees, account inactivity fees, fund withdrawal fees, or demat account maintenance charges. Many brokers list all fees on their website, but it’s still wise to confirm with customer support if anything is unclear.
Some brokers offer global trading accounts that let you access international stock exchanges. Verify whether your broker provides this feature and what additional fees or documentation may be required. In many cases, regulatory bodies in each country have specific guidelines for foreign investors.
Not necessarily. Many brokers allow you to begin trading or investing with a relatively modest sum. Some platforms even provide fractional share investments, letting you invest small amounts in expensive stocks. The key is to start with a well-thought-out strategy and invest what you can afford to lose.