Answer: A crypto wallet is a digital tool or physical device that securely stores your cryptocurrencies, keeps track of your balances, and manages the private keys needed to authorize transactions on a blockchain network. Essentially, it’s like having an online (or offline) “bank account” for your digital assets—except you have complete control over your funds and the keys that unlock them.
Understanding the Concept of a Crypto Wallet
A crypto wallet can be understood as a combination of software and encryption technology that helps you interact with blockchain-based assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies. It provides you with both public and private keys, which are essential for sending, receiving, and safeguarding your digital funds.
Key Points
- Public Key: Think of it like a bank account number. This is your wallet address that others use to send you cryptocurrency.
- Private Key: Comparable to a secret PIN. This must never be shared because it grants the authority to move funds.
These keys collectively form your “account” on any given blockchain. According to Coinbase, having a secure wallet is critical to protect your investments and maintain control over your digital assets.
Main different types of crypto wallets
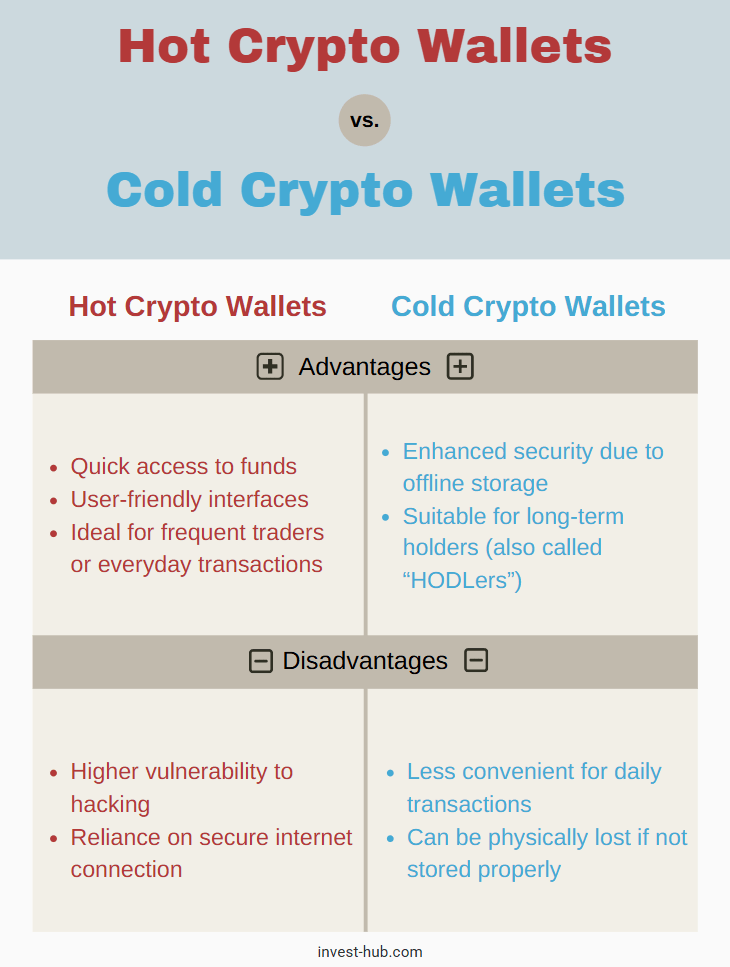
When it comes to cryptocurrency wallets, there is a broad classification: hot wallets (online) and cold wallets (offline). Each has advantages and drawbacks depending on your security needs and how frequently you trade.
Hot Crypto Wallets
Hot wallets are software-based wallets that remain connected to the internet. They can be web apps, mobile apps, or desktop applications.
- Advantages
- Quick access to funds
- User-friendly interfaces
- Ideal for frequent traders or everyday transactions
- Disadvantages
- Higher vulnerability to hacking
- Reliance on secure internet connection
Common hot wallets include web-based wallets like MetaMask or hosted wallets offered by exchanges such as Coinbase.
Cold Crypto Wallets
Cold wallets store your private keys offline, drastically reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
- Advantages
- Enhanced security due to offline storage
- Suitable for long-term holders (also called “HODLers”)
- Disadvantages
- Less convenient for daily transactions
- Can be physically lost if not stored properly
Cold wallets may take the form of paper wallets (simply printing your private keys on paper) or specialized hardware devices.
Types of Crypto Wallets: Hardware Wallet vs. Software Wallet
Hardware wallet devices, such as Trezor or Ledger, are considered one of the safest ways to store cryptocurrency because they keep private keys offline. Meanwhile, a software wallet can be a desktop program or mobile app. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Features | Hardware Wallet | Software Wallet |
| Security | Very high (offline storage) | Moderate (online exposure) |
| Convenience | Requires physical device | Accessible via phone or computer |
| Price | Typically costs $50–$200. | Often free to download |
| Ideal Users | Long-term holders and security-focused | Frequent users/traders who value accessibility |
Hardware wallets are a strong choice for storing large amounts of cryptocurrency, while software wallets are perfect for day-to-day use and smaller balances.
What Is a Wallet Address in Crypto?
A wallet address in crypto is a string of alphanumeric characters that represents your destination for crypto transactions. When someone wants to send you cryptocurrency, they will send it to this address.
How a Wallet Address Is Generated
- Public Key Derivation: Typically, your public key goes through a hashing process to produce a shortened wallet address. This ensures ease of use and adds an extra layer of security.
- Format Variation: Different blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin vs. Ethereum) use distinct address formats. For Bitcoin, addresses often start with “1” or “3,” while Ethereum addresses start with “0x.”
The Importance of Accurate Addresses
If you make a mistake when copying or typing a wallet address—like missing a character—your cryptocurrency could be sent to the wrong place or potentially be lost forever. Many wallet apps include QR codes or copy-paste features to minimize errors.
The Role of Private and Public Keys in a Crypto Wallet
Every cryptocurrency wallet consists of a pair of keys: a public key (shareable) and a private key (secret).
- Public Key: Allows others to view your transactions or send you funds without controlling your wallet.
- Private Key: Enables you to sign transactions, effectively proving ownership of the funds.
Ensuring Private Key Security
- Use Strong Passwords: If your wallet supports password encryption, choose a long, complex password.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Public networks can be compromised, risking your wallet’s security.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of protection whenever you access the wallet.
Most experts recommend storing your private key in a secure location and using hardware wallets for the highest level of security.
How to Set Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet
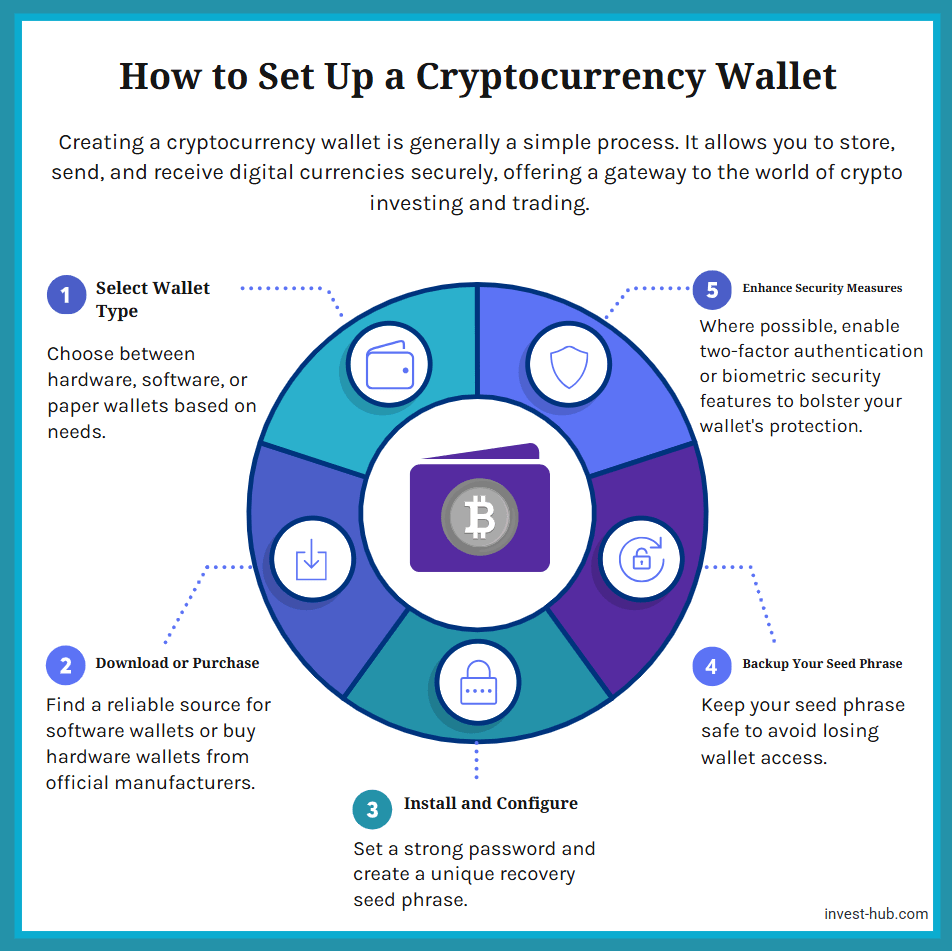
Setting up a cryptocurrency wallet is usually straightforward, especially for software-based options.
- Choose a Wallet Type: Decide between hardware, software, or a paper wallet based on your needs.
- Download or Purchase: For software wallets, find a reputable site or app store. For hardware wallets, buy from official vendors.
- Install or Initialize: Follow the on-screen prompts, create a strong password, and generate your seed phrase (recovery phrase).
- Backup Your Recovery Phrase: This is crucial. If you lose it, you may permanently lose access to your wallet and funds.
- Enable Security Features: 2FA or biometric authentication (where available) can strengthen protection.
Example Recovery Phrase of a Crypto Wallet
A wallet might generate a sequence of random words like:
“maple, vintage, robust, clarity, index, orchard, spring, puzzle, blouse, theater, digital, cushion”
Keep this phrase offline and hidden. It’s your lifeline to restore wallet access if your device is lost or damaged.
Managing Your Crypto Assets in a Wallet
Once your wallet is set up, you can buy, send, or receive cryptocurrency.
- Buying: Exchanges or Binance let you purchase crypto using fiat currency (USD, EUR, etc.) and then transfer it to your wallet.
- Sending: Copy the recipient’s wallet address, enter it into your send interface, confirm the transaction fee, and authorize with your private key or password.
- Receiving: Provide your address or use a QR code so others can send funds to your wallet.
Security Measures and Best Practices
Cryptocurrency is built on decentralized networks, meaning there’s no central authority to help you recover lost funds or keys. Following strict security practices is essential.
Use a Cold Wallet for Large Balances
If you own significant amounts of cryptocurrency, it’s recommended to keep most of it in a cold wallet (e.g., hardware wallet). Hot wallets are convenient but inherently more vulnerable to hacking attempts.
Stay Vigilant Against Scams
- Phishing Sites: Always check URLs carefully. Scammers create fake websites that look like exchange or wallet services.
- Suspicious Links: Never click unsolicited links in emails or social media messages relating to crypto.
- Social Engineering: No legitimate organization will ask for your private key, seed phrase, or wallet password.
Pro Tip: Always verify the authenticity of websites and wallet software before downloading, installing, or transferring funds.
Common Myths About Crypto Wallets
There are various misconceptions around cryptocurrency wallets. Let’s clear some of them up:
- Myth: “All crypto wallets are the same.”
- Fact: Wallets differ in security, convenience, and compatibility with various blockchains.
- Myth: “Crypto stored on an exchange is in my personal wallet.”
- Fact: When you hold funds on an exchange, you typically don’t control the private keys. The exchange does.
- Myth: “A wallet holds physical cryptocurrency.”
- Fact: There’s no physical coin. A wallet only stores private keys and addresses on a blockchain.
Practical Tips for Beginners
- Start Small: Before going “all in,” try storing a small amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to understand how transactions work.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your digital assets in one basket. Spread out between different wallets for security.
- Stay Updated: The crypto landscape evolves quickly. Follow reputable sources for the latest wallet tech and best practices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Crypto Wallets
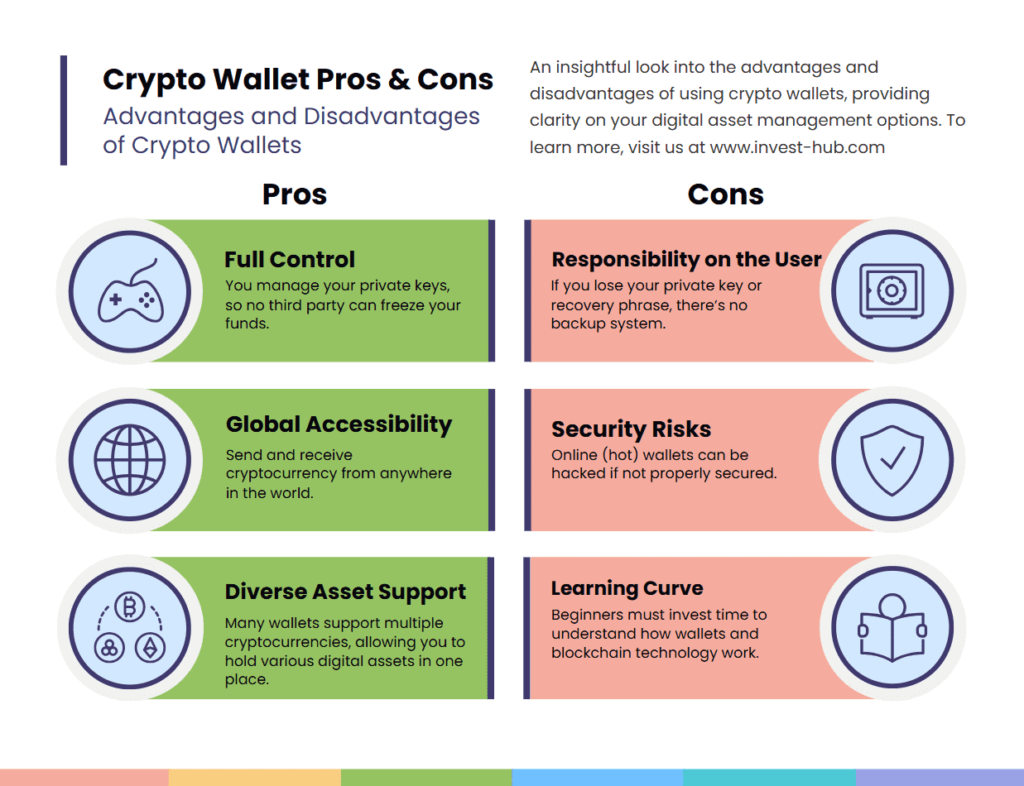
Crypto Wallets Advantages
- Full Control: You manage your private keys, so no third party can freeze your funds.
- Global Accessibility: Send and receive cryptocurrency from anywhere in the world.
- Diverse Asset Support: Many wallets support multiple cryptocurrencies, allowing you to hold various digital assets in one place.
Crypto Wallets Disadvantages
- Responsibility on the User: If you lose your private key or recovery phrase, there’s no backup system.
- Security Risks: Online (hot) wallets can be hacked if not properly secured.
- Learning Curve: Beginners must invest time to understand how wallets and blockchain technology work.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Even the most prepared user can encounter bumps along the way.
- Lost Password or Seed Phrase
- Solution: Unfortunately, if you lose your recovery phrase, you can’t restore your wallet. Always keep multiple secure backups.
- Transaction Delays
- Solution: Network congestion often causes delays. Increasing the transaction fee can speed things up, depending on the wallet.
- Unsupported Tokens
- Solution: Check wallet compatibility before sending tokens. Sending unsupported tokens to a wallet may result in permanent loss.
Conclusion of What Is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is an indispensable tool for anyone looking to invest in or use cryptocurrency. Whether you choose a cold wallet for long-term storage or a hot wallet for frequent transactions, understanding how wallet addresses, public and private keys, and security measures work is essential. By selecting the right type of cryptocurrency wallet for your needs and following best practices, you can confidently explore the world of digital assets while keeping your investments safe.
If you’re ready to take control of your crypto journey, start by testing a software wallet with a small deposit, learn the basics, and then consider upgrading to a hardware wallet for more robust protection. Your wallet is your gateway to the decentralized world—treat it with care, and it will serve as a secure foundation for all your crypto-related endeavors.
What Is a Crypto Wallet FAQ
Not necessarily. Many wallets are multi-currency. However, always check compatibility. Some wallets only support a limited range of coins.
An exchange account holds crypto on your behalf. A wallet gives you full control over your private keys and, hence, your funds.
No. If you lose your private key or recovery phrase, you typically cannot regain access to your wallet or funds.
A hardware wallet is generally considered the safest option for long-term storage due to its offline nature.
They are pseudonymous. While wallet addresses do not directly reveal personal details, transactions are recorded on a public ledger.
It’s often safer to distribute your crypto across multiple wallets. Diversifying storage reduces the risk of a single point of failure.





