What Is a Trading Broker?
A “trading broker” is a professional entity or firm that facilitates the buying and selling of financial instruments on behalf of individuals or institutions.
In essence, brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the financial markets. They ensure that transactions are executed smoothly, securely, and in compliance with applicable regulations.
Key Functions of a Trading Broker
- Intermediary Role: Connect traders with the financial markets.
- Transaction Execution: Ensure trades are executed securely and in line with regulations.
- Tools and Platforms: Provide platforms and services for trading.
- Access to Assets: Enable investment in stocks, currencies, commodities, and more.
Why It Matters
Understanding what a trading broker is remains crucial for anyone looking to participate in financial markets. Choosing the right broker can significantly impact your trading experience and potential success.
Introduction to Trading Brokers
Trading brokers play a crucial role in the global financial system. They act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers in various markets such as stocks, forex, commodities, and other securities.
Primary Functions of a Broker
- Facilitating Orders: Brokers help place and execute buy and sell orders.
- Securing Ownership Transfer: They provide a secure channel for transferring ownership of financial instruments.
- Maintaining Market Orderliness: By connecting buyers and sellers efficiently, brokers ensure transparency and help sustain an orderly marketplace.
Beyond Trade Execution
Many brokers offer more than just trade execution. They often provide features that simplify the trading experience, such as:
- Research Reports
- Educational Resources
- Market Analysis Tools
- Personalized Investment Advice (in some cases)
Types of Brokers
The level of support and services offered can differ significantly, depending on the type of broker. Below is a quick comparison:

| Type of Broker | Key Features | Services Offered |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Service Broker | – Provides in-depth advisory services – Manages portfolios | – Detailed research reports – Personalized investment advice – Comprehensive portfolio management |
| Discount Broker | – Primarily focuses on trade execution – Lower fees | – Basic trade execution – Minimal advisory services – Usually offers online platforms |
The Evolving Role of Brokers
Modern financial markets are complex. As a result, brokers have evolved from mere intermediaries into comprehensive resource hubs. They often provide:
- User-Friendly Platforms: Streamlined interfaces that make it easier to place trades.
- Research Tools & Market Data: Critical information that helps traders make informed decisions.
- All-in-One Services: Combining tools, data, and educational resources under one platform.
By offering these resources, brokers simplify the trading process and encourage a wider range of participants to enter financial markets.
Key Takeaway
For anyone planning to trade—be it stocks, currencies, or other assets—understanding the value and function of trading brokers is vital. Knowing how brokers operate, what services they provide, and how they can support your trading journey is the first step toward responsible and successful trading.
What Is the Meaning of Broker in Trading?
When people first explore financial markets, they often ask: “What is the meaning of broker in trading?”
At its core, a broker is a licensed individual or firm authorized to buy and sell securities or other financial instruments on behalf of clients.
Main Function
A broker’s main function is to facilitate deals between buyers and sellers.
They ensure that each party’s interests and obligations are met.
Brokers operate in various markets—such as equities, forex, and commodities—using their market expertise to execute trades accurately and efficiently.
Access to Markets
A critical role of a broker is providing traders and investors with access to markets they might not be able to reach independently.
Financial markets can be massive and fragmented.
Most retail traders lack direct access to exchanges.
Brokers bridge this gap by offering platforms that link individual traders to these large, often global marketplaces.
Compliance and Security Brokers handle important tasks such as:
- Complying with regulatory standards
- Safeguarding client funds
- Executing trades in a timely manner
This helps maintain a regulated, transparent, and supportive environment for trading.
Additional Services
Beyond acting as intermediaries, brokers can also deliver extra value.
They may provide:
- Market research
- Analytics tools
- Educational content
Depending on the service model, clients might receive basic trade execution or comprehensive portfolio management.
Examples of Broker Service Models
| Type of Broker | Potential Services Offered |
|---|---|
| Full-Service Broker | Advanced software for charting, risk management, and automated trading |
| Discount/Execution-Only | Emphasis on cost-effective, fast trade execution |
| Advisory Broker | Personalized advice, customer support, and portfolio management |
Choosing the Right Broker
Some brokers focus on advanced software for automated trading.
Others emphasize customer service and personalized advice.
It’s essential for new traders to understand what a broker does.
This ensures they choose a broker that aligns best with their goals.
Understanding “what is the meaning of broker in trading” goes beyond a simple definition.
A broker is vital for ensuring trades occur in a regulated, transparent environment.
This fundamental knowledge helps new traders navigate the industry confidently and select the appropriate service level.
Understanding What a Broker is in Trading
According to AngelOne, A broker acts as a conduit between market participants, ensuring every trade finds a counterparty. This often involves matching buy orders with sell orders—or vice versa—so trades are completed without delay.
Key Roles of a Broker
- Maintain Market Liquidity
Brokers make it easier for investors to find someone to take the other side of a transaction. This constant matching of orders helps keep the market liquid. - Handle Back-End Tasks
They maintain client accounts, track regulatory and exchange rules, and protect client funds. These services make trading more efficient and less risky. - Safeguard Client Funds
Some brokers hold client funds in segregated accounts. This practice, often mandated by regulators, helps protect investors’ money even if the brokerage faces financial difficulties.
Modern Broker Services
Suitable for All Traders:
Whether you are a short-term day trader or a long-term investor, these tools can simplify the trading process and potentially improve your outcomes.
Trading Platforms:
Many brokers provide user-friendly platforms with real-time market data, charting tools, and automated trading algorithms.
News and Analytics:
Some platforms integrate news feeds and analytics software, helping traders spot trends or react quickly to market developments.
Types of Trading Brokers
According to Groww, There are various types of trading brokers. Each one caters to different trading styles, investment goals, and levels of experience. Choosing the right broker is crucial because the services, fees, and platforms they offer can heavily influence your overall success.

Full-Service Brokers vs. Discount Brokers
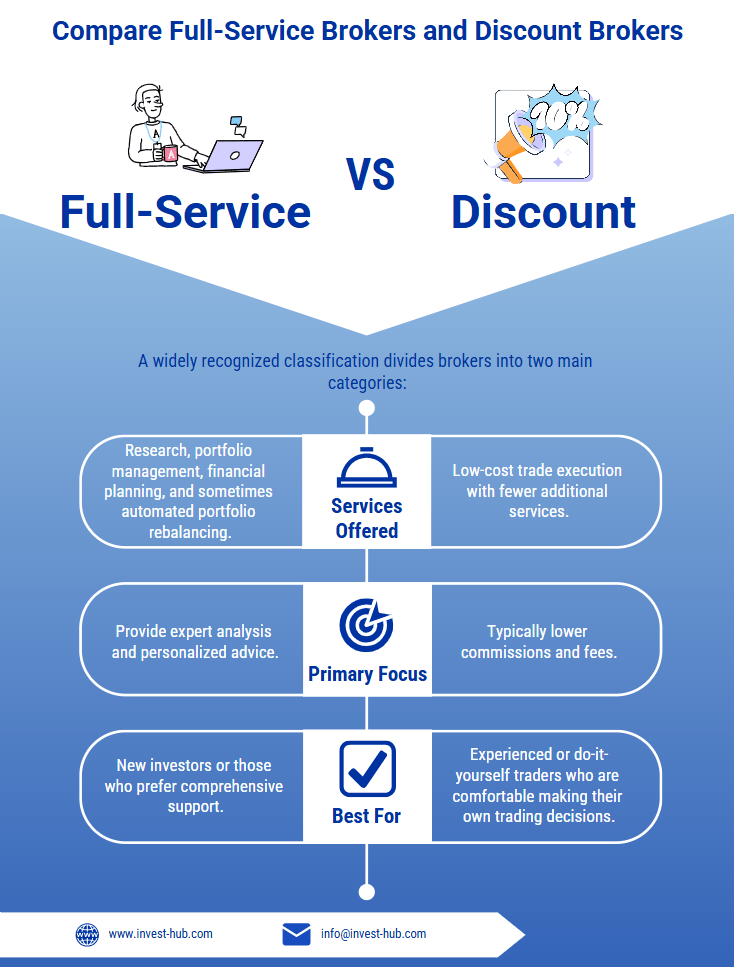
A widely recognized classification divides brokers into two main categories:
- Full-Service Brokers
- Services Offered: Research, portfolio management, financial planning, and sometimes automated portfolio rebalancing.
- Guidance: Provide expert analysis and personalized advice.
- Best For: New investors or those who prefer comprehensive support.
- Discount Brokers
- Primary Focus: Low-cost trade execution with fewer additional services.
- Fees: Typically lower commissions and fees.
- Best For: Experienced or do-it-yourself traders who are comfortable making their own trading decisions.
Key Point: If you need extensive guidance, a full-service broker might be appealing. If you want to minimize costs and handle decisions yourself, a discount broker may be more suitable.
Specialized Brokers
Some brokers specialize in particular markets or instruments:
- Forex Brokers
Focus on the foreign exchange market, providing access to currency pairs and tools tailored for currency trading. - Commodity Brokers
Concentrate on trading commodities like gold, oil, and agricultural products. They often facilitate trades in futures and options markets. - Crypto Brokers
Specialize in digital currencies, offering platforms for buying and selling cryptocurrencies.
Note: Many modern platforms integrate multiple asset classes. This allows you to trade stocks, currencies, and commodities under the same account.
Comparison Table
| Broker Type | Key Services/Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Service Broker | Research, portfolio management, financial planning | Investors wanting expert guidance and comprehensive support |
| Discount Broker | Low-cost trade execution, fewer extra services | Self-directed traders looking to minimize fees |
| Forex Broker | Currency pairs, specialized forex trading tools | Traders focused on the foreign exchange market |
| Commodity Broker | Futures and options in commodities (gold, oil, etc.) | Investors wanting exposure to commodity markets |
| Crypto Broker | Buying and selling digital currencies | Traders/investors interested in cryptocurrencies |
Full-Service Brokers
Full-service brokers are often viewed as the “traditional” brokerage model. They offer a wide array of services beyond simple trade execution, such as financial planning, investment advice, research reports, and portfolio management. These brokers typically target investors who prefer a hands-on, guided experience.
For example, you might consult your broker for recommendations on which stocks to buy or how to balance a portfolio. Some full-service firms also organize seminars, webinars, or one-on-one sessions to educate their clientele about market trends and financial strategies.
One key advantage of full-service brokers is personalized attention. Traders can work closely with assigned account managers or advisors who understand their specific financial goals, risk tolerance, and market preferences. This level of support can be particularly beneficial for new investors who want to build a balanced portfolio with a mix of equities, bonds, and other instruments.
Additionally, many full-service brokers have access to exclusive research teams and proprietary analytics, offering deeper insights into market conditions. These insights can help investors make more informed decisions.
However, all this comes at a cost. Full-service brokers generally charge higher fees and commissions than discount brokers. These costs may include:
- Management fees
- Annual charges
- Transaction-based costs
If you’re an investor who trades infrequently and values professional advice, these higher fees may be justified by the added resources and personalized guidance. On the other hand, if you prefer a do-it-yourself approach and want to minimize trading expenses, a full-service broker might not be the most cost-effective option.
Discount Brokers
Discount brokers have surged in popularity, particularly with the rise of online trading platforms. Unlike full-service brokers, discount brokers primarily focus on executing trades at a reduced cost.
These brokers can charge significantly lower fees and commissions because they often operate online, bypassing many overhead costs associated with physical offices or large advisory teams. As a result, traders—especially those who are more active or have a DIY investing style—can benefit from lower transaction fees and potentially more frequent trades.
One major advantage of discount brokers is accessibility. Most provide user-friendly platforms that allow clients to:
- Place orders
- View market data
- Track portfolios in real-time
These platforms often include advanced charting capabilities, technical analysis indicators, and risk management features, enabling traders to make timely and informed decisions. Because discount brokers cater to a tech-savvy audience, their platforms are frequently updated to keep pace with new trends and technologies.
However, there are some drawbacks. Limited customer support and fewer educational resources can be a challenge for some traders. While certain discount brokers offer educational materials and market analysis, these resources are generally more generalized compared to the personalized advice available from full-service brokers.
The emphasis on low-cost trading means that individuals must be willing to perform their own research and develop their own strategies. This independence can be rewarding for experienced traders or those committed to learning, but it can also be overwhelming for beginners.
What Is a Forex Trading Broker?
The term forex trading broker frequently appears when discussing currency markets. A forex trading broker specializes in facilitating the buying and selling of foreign currencies.
According to IG, the forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily turnover exceeding trillions of dollars. Forex brokers offer traders access to currency pairs—such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, or USD/JPY—allowing them to speculate on the relative performance of one currency against another.
Leverage and Risks
Forex brokers typically provide leveraged trading, enabling traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it also significantly increases risk. This is one of the key differences between forex trading and other financial markets.
Because of this, regulation plays a crucial role in forex trading. Many reputable forex brokers offer negative balance protection, ensuring that traders don’t lose more than their initial deposit.
Trading Platforms and Tools
In addition to trade execution, forex brokers often provide specialized trading platforms designed specifically for currency trading. These platforms may include:
- Advanced charting packages
- Technical indicators for short-term and long-term analysis
- Risk management tools
Since the forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, traders need a platform that can handle fast-moving conditions. As a result, efficient order execution, narrow spreads, and reliable customer support are essential features to look for in a forex broker.
Beyond Currencies: CFDs and Other Instruments
Many forex brokers also offer CFDs (Contracts for Difference) on:
- Commodities
- Indices
- Stocks
This allows traders to diversify their strategies beyond just currency trading.
The Role of Regulation and Licensing
Regulation and licensing are the cornerstones of a trustworthy trading environment. They act as protective measures that safeguard traders from unethical practices and fraudulent operations.
According to Wikipedia and other reputable sources, brokers generally need specific licenses to operate, which vary by jurisdiction. For example:
- In the United States, a broker may require registration with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and membership in the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
- In the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) oversees brokerage activities.
- In Australia, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) plays a similar role.
Why Regulation Matters
Licenses and regulatory adherence serve multiple purposes:
- Financial Security & Risk Management
- Brokers must meet industry standards for financial reporting, capital adequacy, and risk management.
- This minimizes the likelihood of brokers misusing client funds or engaging in excessively risky behavior.
- Transparency & Fairness
- Regulation ensures a clear and transparent trading environment.
- Clients have access to essential details about fees, spreads, and execution policies.
- Transparency promotes fair trading conditions and allows traders to make more informed decisions.
- Dispute Resolution & Investor Protection
- Licensed brokers must comply with dispute resolution processes, such as mediation or arbitration, to address client complaints.
- In some jurisdictions, compensation schemes exist to reimburse traders if a licensed broker fails or goes bankrupt.
Regulation in High-Risk Markets
Regulation is particularly crucial in markets like forex, where high leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Unscrupulous brokers may try to lure traders with unrealistic promises, leading to potential financial losses. Regulatory oversight helps maintain a level playing field and deters malpractice.
How to Verify a Broker’s Regulatory Status
Before committing funds to any brokerage, it’s essential to verify their regulatory status. Investors can typically
Verify credentials with the relevant regulatory authority (e.g., SEC, FCA, ASIC).
Check the broker’s official website for licensing information.
How to Become a Trading Broker
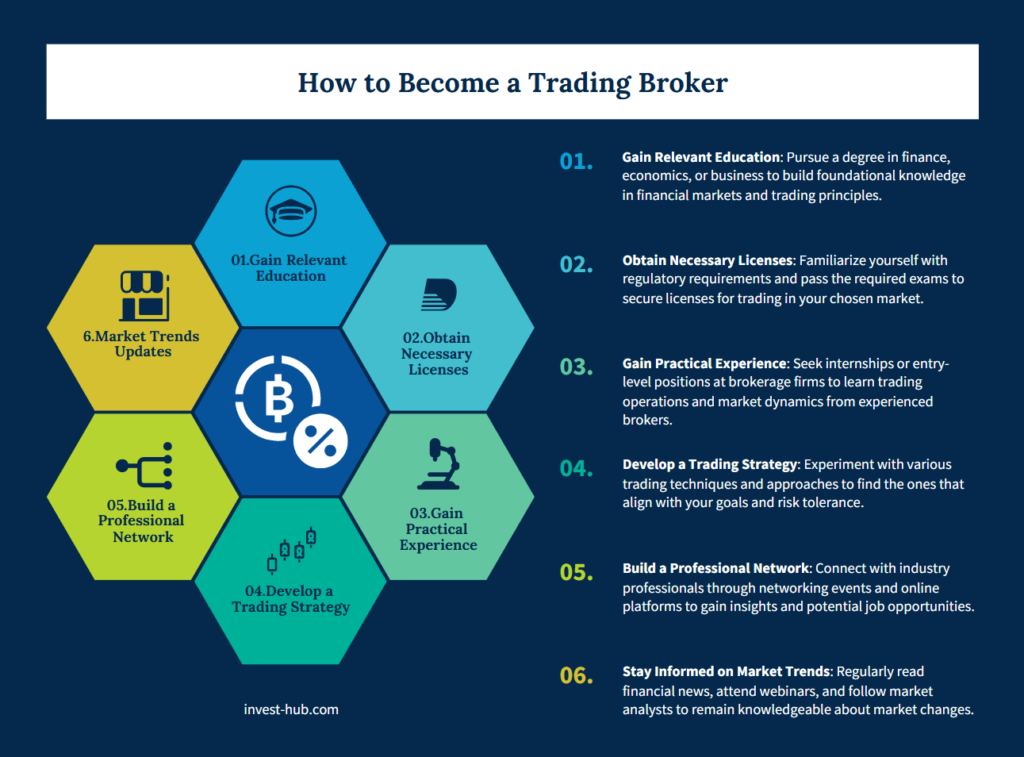
The question of how to become a trading broker is common among individuals who aspire to be intermediaries in financial markets. Becoming a broker is a multifaceted journey that requires educational credentials, practical experience, and relevant certifications.
Whether you plan to specialize in stockbroking, forex, or commodities, you’ll need a solid understanding of financial markets, regulations, and trading strategies.
Choosing the Right Broker for Your Needs
Selecting a brokerage firm is a pivotal decision that can impact your trading performance and overall experience. Several key factors should guide your choice, including fees, customer service, platform features, and asset selection.
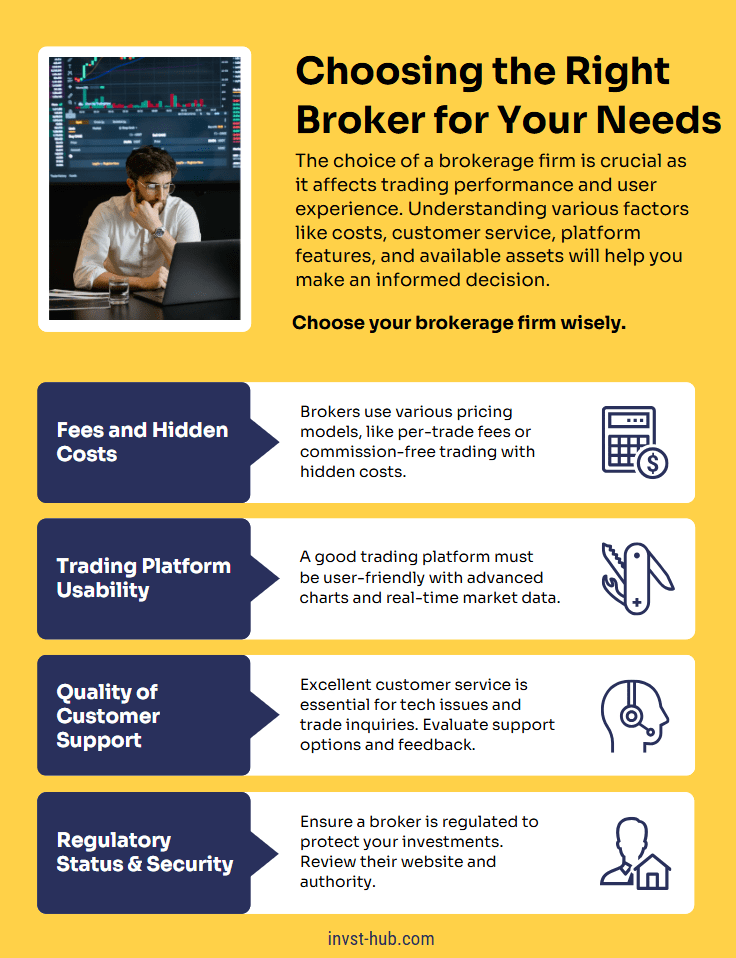
1. Fee Structure and Hidden Costs
Different brokers have varied pricing models:
- Some charge per-trade commissions.
- Others offer commission-free trading but may impose monthly subscription fees or wider spreads.
Additionally, be aware of hidden costs, such as:
- Account maintenance fees
- Withdrawal charges
- Inactivity penalties
To avoid unexpected expenses, always read the fine print before committing to a broker.
2. Trading Platform Usability
A user-friendly trading platform is essential, especially for beginners. A good platform should offer:
- Intuitive navigation
- Robust charting tools
- Real-time market data feeds
Many brokers provide demo accounts, allowing traders to practice strategies in a risk-free environment. If you trade on the go, check whether the broker offers a stable and well-designed mobile app for executing trades and monitoring positions anytime, anywhere.
3. Quality of Customer Support
Reliable customer service can make a significant difference when dealing with technical issues or urgent trade-related questions. Before choosing a broker, consider:
- Available support channels (phone, email, live chat)
- Response times
- Customer reviews and testimonials
Reading online reviews or talking to current or former clients can provide valuable insights into a broker’s responsiveness and reliability.
4. Regulatory Status and Security
Ensuring that a broker is properly licensed and regulated is crucial for your financial security. Brokers operating without regulatory oversight can be risky.
To verify a broker’s legitimacy:
- Check their website for regulatory credentials.
- Confirm the license with the appropriate regulatory authority database.
Common Challenges in Working with a Trading Broker
While trading brokers can provide invaluable services, various challenges may arise in your interactions with them. Being aware of potential pitfalls—such as hidden fees, technical issues, customer service quality, and regulatory concerns—can help you make a more informed decision.
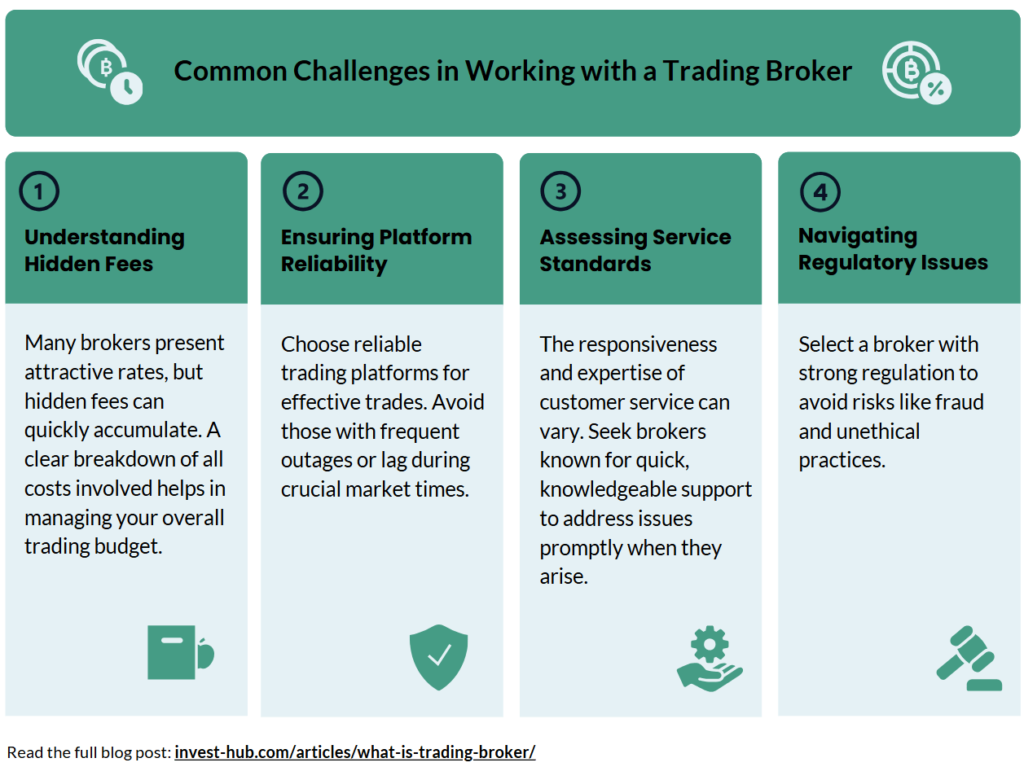
1. Hidden Fees and Complex Pricing Structures
One of the most prevalent issues is the complexity of fee structures. Even if a broker advertises low commissions, additional charges can significantly inflate trading expenses, including:
- Annual maintenance fees
- Withdrawal fees
- Platform subscription costs
Some brokers do not always highlight these hidden costs upfront. Transparent communication about fees is crucial, but it’s ultimately your responsibility to review fee disclosures carefully—especially if you’re a high-volume trader or frequently move funds in and out of your account.
2. Trading Platform Reliability and Performance
In fast-moving markets, platform delays or technical glitches can negatively impact trade execution. Some brokers may experience:
- Server downtime during peak hours
- Delayed order processing
- Platform instability during high market volatility
To avoid these issues, consider:
- Testing a broker’s demo account before committing.
- Reading user reviews that discuss real-world performance.
- Choosing brokers who invest in robust infrastructure and technology.
3. Customer Service Quality
The quality of customer service varies significantly across brokers. While some firms offer 24/7 support with knowledgeable representatives, others may be slow to respond or lack expertise. Poor customer service can lead to:
- Miscommunication and confusion about trades
- Missed opportunities due to delayed responses
- Unresolved disputes that affect account security
Before selecting a broker, ensure they have a dedicated support team that is easily reachable via:
- Phone
- Live chat
4. Regulatory and Security Concerns
Working with an unregulated or loosely regulated broker can expose you to unethical or fraudulent practices. This increases the risk of:
- Unfair trading conditions
- Difficulty withdrawing funds
- Lack of legal protection in disputes
To safeguard your capital, always verify a broker’s regulatory status with reputable authorities, such as:
- SEC & FINRA (U.S.)
- FCA (U.K.)
- ASIC (Australia)
A well-regulated broker provides greater security, transparency, and accountability.
Best Practices for Trader-Broker Relationships
Maintaining a constructive relationship with your broker can enhance your trading experience and improve overall outcomes. Following best practices such as clear communication, regular engagement, and leveraging available resources can help you make more informed trading decisions.
1. Prioritize Transparency
Transparency is the foundation of a strong broker-client relationship. To ensure alignment, you should:
- Communicate your trading goals, risk tolerance, and market interests openly.
- Expect clear, unambiguous information about:
- Fees and commissions
- Order execution policies
- Potential conflicts of interest
A broker who understands your unique needs can provide better services and recommendations tailored to your trading strategy.
2. Maintain Regular Communication
Whether you are a high-frequency trader or a long-term investor, staying in touch with your broker can be beneficial. Many brokers offer:
- Market research reports
- Webinars and educational content
- Industry trend discussions
Participating in these resources can broaden your knowledge and help refine your trading strategies. If you have questions or concerns, reaching out promptly can prevent small misunderstandings from escalating.
3. Utilize Broker-Provided Tools and Analytics
Many brokerages offer advanced trading tools, including:
- Charting software and technical indicators
- Fundamental research reports
- Risk management features
Even if your broker does not provide in-depth research, they may have partnerships with external platforms that offer valuable insights. Taking advantage of these resources can help you:
✅ Identify new market opportunities
✅ Improve risk management
✅ Optimize your trading strategies
4. Stay Updated and Respect Regulatory Requirements
Continuous learning is crucial in the ever-evolving financial markets. Keep track of your broker’s updates on:
- Platform enhancements
- Regulatory changes
- New asset offerings
These updates could introduce new opportunities or streamline your trading workflow. At the same time, respect your broker’s expertise and regulatory constraints. Brokers must comply with strict regulations, which may require:
- Additional paperwork
- Limitations on certain trade types
Understanding these constraints fosters a mutually beneficial relationship.
Conclusion: The Importance of Brokers in Trading
Brokers play a crucial role in financial markets, acting as intermediaries that connect buyers and sellers while providing the tools and resources necessary for efficient and transparent trading.
By now, you have a comprehensive understanding of what a trading broker is and the various types of brokerage services available—from full-service firms that provide personalized advice to discount brokers that prioritize low-cost trade execution.
The Importance of Regulation and Broker Support
Regardless of whether you are trading in stocks, forex, or commodities, choosing a reliable, well-regulated broker is essential. Regulation and licensing ensure that brokers operate under strict guidelines, fostering fairness and transparency in the market.
Beyond regulation, a broker’s support system can significantly impact your trading success. Features such as:
- Educational materials
- Advanced trading platforms
- Responsive customer service
can help you navigate the complexities of trading and refine your strategies.
The Importance of Due Diligence
Selecting the right broker requires careful research. Factors like fee structures, platform reliability, customer service, and regulatory standing should be evaluated before making a commitment. Due diligence is not just recommended—it is imperative.
Additionally, maintaining open communication and mutual respect with your broker can enhance your trading experience and lead to more informed decision-making.
FAQ
While it’s theoretically possible in some markets—particularly decentralized ones like certain cryptocurrency exchanges—most traditional assets, including stocks and bonds, require a broker to access primary exchanges. Even in cases where direct transactions are allowed, individual traders typically benefit from the broker’s infrastructure, such as real-time data feeds and compliance safeguards.
Brokers often earn revenue through multiple channels, including commissions, spreads, platform fees, margin interest, and other administrative charges. Some even offer premium services—like managed portfolios—for which they charge additional fees. Q: How do I check if my broker is regulated?
A: You can verify a broker’s regulatory status by consulting the website of the relevant financial authority in your region. Legitimate brokers usually list their registration details and license numbers publicly. Cross-referencing this information with official regulatory databases helps confirm authenticity.
The difference often lies in the range of services offered, operational costs, and business models. Discount brokers primarily provide self-directed platforms, which lowers overhead costs and allows for reduced fees. Full-service brokers invest in advisory and research teams, justifying higher charges.
Technology is central to today’s trading environment. Many brokers now offer intuitive digital platforms with tools for analysis, automated trading, and robust mobile apps. This tech-driven approach not only speeds up trade execution but also allows for greater flexibility and convenience.





