If you’ve ever stepped into the world of trading—especially Forex—you’ve probably heard about leverage and wondered, “So Why do brokers give us leverage?” I’ve asked myself the same question. Leverage is that fascinating concept that lets you control bigger positions in financial markets, even if you don’t have a big bag of money in your account. It can boost your potential profits in a flash, but let’s not forget it can also ramp up your losses just as quickly. In this quick guide, I’ll walk you through what leverage is, why brokers offer it, and how to handle it responsibly. By the time we’re done, you’ll (hopefully) feel more confident about using leverage in your trading.
Answer: Brokers offer leverage primarily to attract more traders, boost trading volume, and earn additional revenue through fees or spreads on larger trades. By letting traders control bigger positions with less initial capital, brokers create an enticing environment where potential profits are higher—though so are the risks. This win-win approach enables brokers to stand out in a competitive market while giving traders the chance to engage with significant market moves, even with smaller accounts.
Introduction to Leverage
Setting the Stage for Forex Trading
Forex trading often involves swapping huge amounts of currencies. These numbers can be so large that they can make your head spin.
To allow more people to participate, brokers introduce a tool called “leverage.” According to SBI Securities, leverage is the opportunity to open trades that are far larger than your normal account balance would allow.
Let’s say you only have a small amount of money to start with. Leverage helps you jump into the big leagues (sort of). It’s like borrowing money from the broker so you can trade as if you had a heftier account.
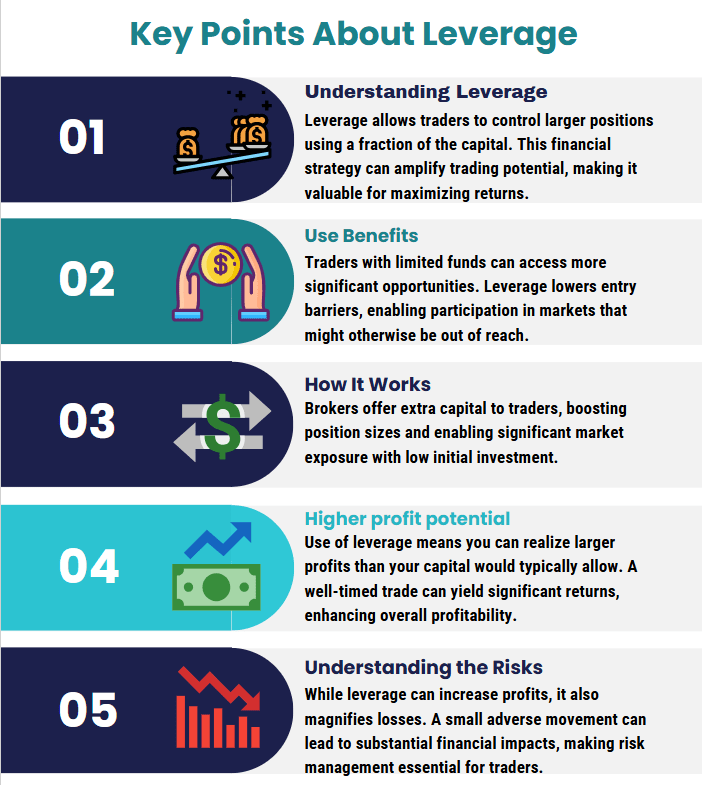
The Importance of Leverage in Financial Markets
Leverage isn’t just a Forex thing. You’ll see it in equity, commodity, and derivative trading too. Groww points out that leverage can supercharge your buying power, which is fantastic if your trades go the way you want. But remember, markets can be as unpredictable as the weather; a small shift in the price can magnify losses, too. That’s why leverage is often described as a double-edged sword—one that can make or break a trader much faster than traditional, no-leverage positions.
What Is Leverage in Forex for Beginners?
Basic Definition and Core Concepts
If you’re brand new to Forex, leverage simply means you’re borrowing funds from your broker to trade a bigger position than your account balance could handle on its own. For example, with 1:100 leverage, every dollar you have in your account gives you the power to trade $100. This can help you capitalize on those tiny fluctuations in currency pairs. But just like a roller coaster, while the ups can be thrilling, the downs can be brutal—and the speed is cranked up by leverage.
Key Terminology (Margin, Buying Power, etc.)
You’ll hear words like “margin,” “buying power,” and “maintenance margin” thrown around. Margin is basically the “good faith” deposit you need to open a trade. Buying power is how much total trading value you can control with both your own funds and the borrowed amount. If your account balance dips below a certain threshold (the maintenance margin), you might get that dreaded “margin call,” forcing you to either pony up more cash or close some positions before things get worse.
Why do brokers give us leverage in Forex?
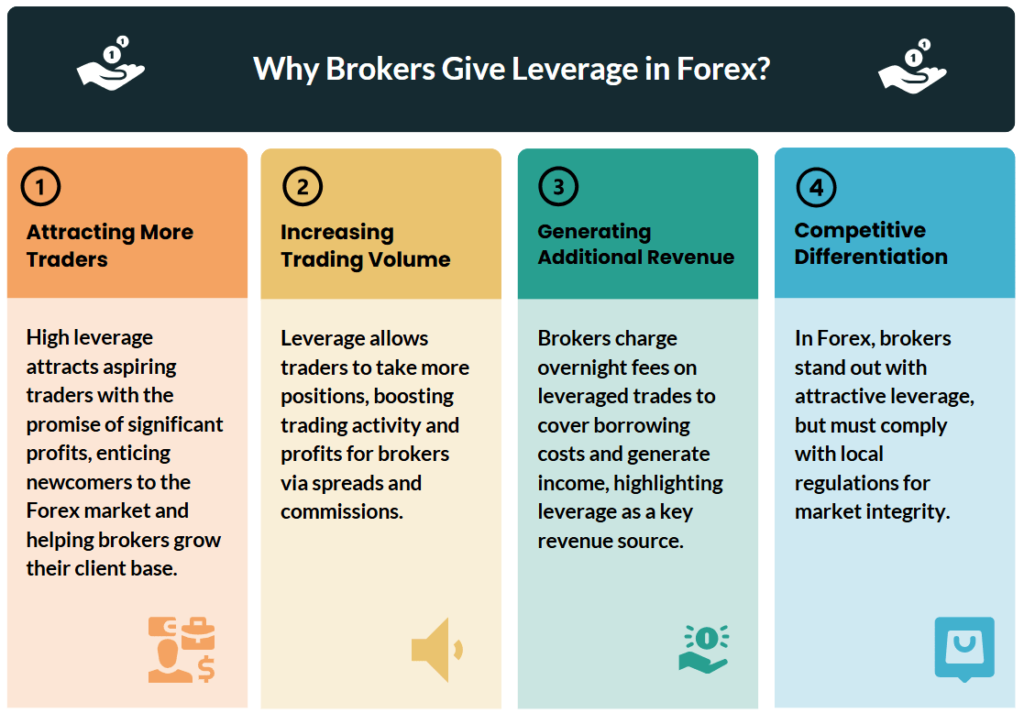
Attracting More Traders
Let’s be real: high leverage is a shiny lure for new traders. People see those big potential gains and think, “Sign me up!” Brokers know this. Offering hefty leverage can bring in folks who otherwise couldn’t afford to dive in. It creates a buzz, opens the door for more retail traders, and adds to the overall excitement in the market.
Increasing Trading Volume
Beyond the initial attraction, leverage makes it easier for traders to keep opening new positions. More trades mean more volume, and that volume often translates into spreads and commissions—essentially the broker’s bread and butter. Leverage.Trading mentions how this cycle of higher trading volume can really pump up a broker’s revenue, which is why many firms advertise striking ratios like 1:50, 1:100, or even 1:1000.
Generating Additional Revenue (Interest & Fees)
Spreads and commissions are just part of the story. Brokers may also charge overnight financing fees (often called “swap” fees) if you hold your leveraged position past the close of the trading day. These fees help the broker cover their own borrowing costs, and sometimes they keep a little profit, too. So, from a broker’s perspective, leverage isn’t merely a marketing gimmick—it can be a steady source of income.
Competitive Differentiation
In a crowded space, brokers try to stand out by offering better trading platforms, tighter spreads, or eye-catching leverage ratios. Some brokers deliberately push those ratios up—like 1:500 or 1:1000—to snag thrill-seeking traders who are comfortable with bigger risks. Of course, different regions have different regulations that keep leverage under control (and for good reason). So if you’re seeing a broker touting off-the-charts leverage, double-check they’re playing by the local rulebook.
Leverage in Forex Example
Leverage 1:1000 Meaning
1:1000 means that for every $1 in your account, you can control $1,000 in trades. Let’s say you deposit $100; you suddenly have the ability to open positions worth $100,000. That’s some serious buying power! Regulators often place a cap on leverage to protect retail traders from going broke overnight. With 1:1000 leverage, even a tiny price fluctuation in the wrong direction can drain your account faster than you can say, “Wait, what just happened?”
Practical Scenarios Demonstrating Gains & Losses
Picture this: you have $1,000 in your account and use 1:100 leverage to open a $100,000 position on EUR/USD. If the market shifts just 1% in your favor, you’ve doubled your account to $2,000. Not bad, right? But if it drops by the same 1%, you’re basically wiped out. Under high leverage, even these modest price movements can turn into pivotal moments. It’s like walking a tightrope without a safety net.
Understanding Risk vs. Reward
If you’re thinking, “Well, that’s terrifying,” you’re not alone. Leverage magnifies everything—good and bad. It can catapult your winnings, but it can also crush you if you’re not careful. IG underscores that to manage this seesaw, you need a solid plan, possibly with stop-loss orders or strict risk management rules. In other words, respect leverage, or it’ll demand respect from you.
How Can Leverage Impact Your Trading?
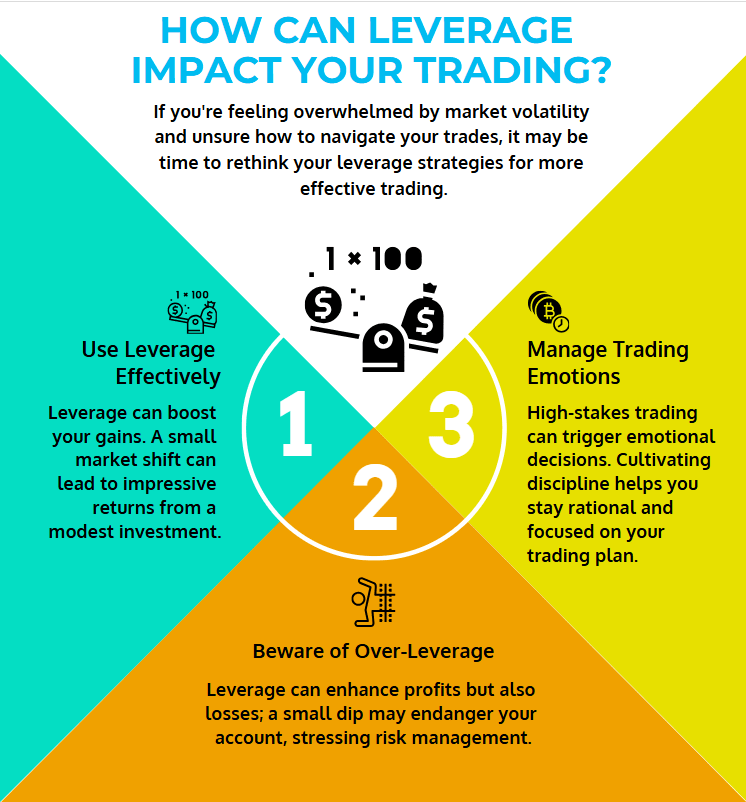
Amplifying Potential Gains
Let’s start with the good news. If the market so much as sneezes in your favor, you could see returns that make you feel like a genius. A modest 0.5% move could lead to a 10% gain on your account, depending on how much leverage you’re using. This can be especially tempting if you’ve got a small account and are aiming for big results. But let’s keep a balanced view here…
Amplifying Potential Losses
…Because losses get supercharged too. Even a tiny move in the wrong direction can hurt—big time. Another 1% drop in the currency pair could blow up your account if you’re heavily leveraged. This is precisely why many regulators set strict limits on maximum leverage. The bigger the leverage, the smaller the margin for error.
Psychological Influence on Trading Decisions
Oh, and let’s not ignore the mental toll. When you know your trades can swing hundreds or thousands of dollars on a dime, the stress can be intense. You might get tempted to revenge-trade after a loss or go “all in” on a hunch—both of which can end badly. Emotional discipline is a game-changer here. I’m no psychologist, but I’ve seen enough to know that fear and greed can wreak havoc if you don’t keep them in check.
Risks and Considerations
Risk of Margin Calls
A margin call is what happens when your account balance slips below a certain point, and the broker says, “Okay, that’s enough. I’m closing out your trades.” This is how brokers protect themselves from losing money they lent you. In fast-moving markets, margin calls can happen before you even realize your account is in the danger zone. Best to keep an eye on your open positions and margin levels so you’re not caught off guard.
Overtrading and Emotional Decision-Making
Ever feel that itch to place “just one more trade” because, hey, the money’s basically there for the taking? That’s overtrading, and it’s often fueled by leverage. The bigger your position sizes, the more intense your emotional roller coaster. Overtrading can quickly drain your capital if you’re hopping into trades for all the wrong reasons—like FOMO or the need to “win back” losses. This is where a strict trading plan can be your saving grace.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Depending on where you live, you might notice different rules about leverage. In the U.S., for example, the National Futures Association (NFA) caps retail Forex leverage at 1:50 for major currency pairs. SEBI in India also sets margin rules for brokers operating there. These regulations aim to protect traders (especially newbies) from biting off more risk than they can chew. Make sure you pick a broker that’s legit in your region—that way, you know they’re playing by the rules and not giving you unrealistic or predatory offers.
Best Practices for Managing Leverage
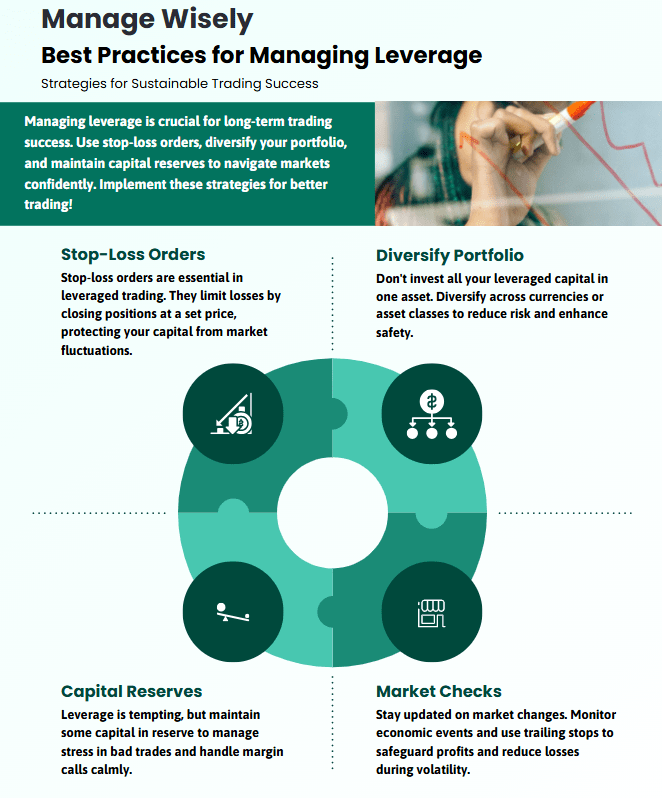
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss is your friend when you’re using leverage. It automatically closes your position if the market hits a certain price, thereby limiting your downside. IG calls it the cornerstone of good risk management, and I fully agree. If you’re like me, you probably don’t have time to sit and monitor every tick. A properly placed stop-loss ensures one bad trade won’t wipe out your entire account.
Diversifying Your Portfolio
It’s easy to dump all your leveraged capital into one “sure thing,” but guess what? The market doesn’t owe us anything. Diversifying across currency pairs or even into other asset classes—like metals or indices—can help cushion the blow if one trade goes sour. It’s a classic risk management tactic: don’t put all your eggs in one basket.
Maintaining Adequate Capital Reserves
Just because your broker says you can use 1:500 leverage doesn’t mean you should go full throttle. Having a buffer of unallocated capital can prevent panic when trades head south. Many experienced traders prefer lower leverage or keep extra funds on the sidelines, so they don’t get blindsided by a margin call. It’s boring, maybe, but boring can be good in trading.
Regularly Monitoring Market Conditions
Markets can change on a dime—geopolitical events, central bank announcements, you name it. When you’re leveraged, these moves get magnified. Keep an eye on economic calendars, big news releases, and technical indicators. Some traders even use trailing stops to lock in profits as the market moves in their favor. Vigilance can be the difference between a modest pullback and a catastrophic loss.
Conclusion on Why Broker Gives Leverage?
Balancing Opportunity and Risk
Leverage offers the chance to amplify your profits, but it can just as easily magnify your losses. From margin calls to sudden emotional swings, using borrowed capital demands a level-headed approach. The goal is to ride the wave of opportunity without getting wiped out by risk. With the right balance of discipline and awareness, leverage can become a helpful ally rather than your worst enemy.
Frequently Asked Questions on Why do brokers give us leverage?
Because it attracts more traders, ramps up trading volume, and generates extra revenue. It’s also a way brokers stand out in a competitive market.
It multiplies gains and losses, so be prepared for both.
How to manage it? Use stop-losses, diversify, keep a cushion of capital, and stay informed about market events.
Use stop-losses, diversify, keep a cushion of capital, and stay informed about market events.
teady, consistent performance matters way more than short-lived, high-risk wins.





